Main Business Scope
 Organic certification (cultivated crops, edible mushrooms)
Organic certification (cultivated crops, edible mushrooms) Organic certification (wild collection)
Organic certification (wild collection) Organic certification (livestock and poultry farming)
Organic certification (livestock and poultry farming) Organic certification (aquaculture)
Organic certification (aquaculture) Organic certification (food processing)
Organic certification (food processing) Organic certification (textiles)
Organic certification (textiles) Organic certification (operation, trade)
Organic certification (operation, trade) Organic assessment (inputs)
Organic assessment (inputs) Organic catering certification (hotels, restaurants)
Organic catering certification (hotels, restaurants)

Introduction to Organic Products in China
organic production
An agricultural production method that follows specific production principles, does not use genetically engineered organisms and their products, does not use chemically synthesized pesticides, fertilizers, growth regulators, feed additives and other substances, follows the laws of nature and ecological principles, coordinates the balance between planting and breeding, and maintains a sustainable and stable production system.
Organic products:
Refers to organically produced and processed products for human consumption and animal consumption.
【Production materials requirements for planting industry】:
1. Seeds: Do not use coated seeds or non-GMO seeds, and do not mix seeds with chemical drugs before use;
2. Fertilizer: Chemical fertilizers are prohibited. Homemade farmyard manure, organic fertilizer, and biological fertilizer can be used;
3. Pesticides: Chemical pesticides, chemical herbicides and hormones are prohibited. The use of biological pesticides, plant-based pesticides and mineral pesticides is allowed, and physical and biological control are encouraged.
The pesticides permitted for use are:
Insecticides: azadirachtin, natural pyrethrin (pyrethrum), matrine and oxymatrine, rotenone (such as hairy derris), osthole, vegetable oils (such as peppermint oil, pine oil, coriander oil), gelatin, paraffin oil, natural attractants and nematicides (such as marigold, cosmos, mustard oil), plant extracts with repellent effects (garlic, mint, pepper, pepper, lavender, bupleurum, wormwood extracts). Fungi and fungal extracts (such as Beauveria bassiana, Verticillium, Trichoderma, etc.), bacteria and bacterial extracts (such as Bacillus thuringiensis, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus licheniformis, Pseudomonas fluorescens, etc.), viruses and virus extracts (such as nuclear polyhedrosis virus, granulovirus, etc.).
Sterilization: sulfur, copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture, lime sulfur, lime water, potassium bicarbonate, calcium hydroxide, ethanol, salt water, alum, quartz sand, berberine (extracts from Coptis chinensis, Phellodendron chinense, etc.), physcion methyl ether (extracts from rhubarb, Polygonum cuspidatum, etc.), natural acids (such as vinegar, wood vinegar and bamboo vinegar), mushroom proteoglycans (mushroom extracts).
Weed killers: Wood vinegar and bamboo vinegar
4. Agricultural film: Do not use chlorine-containing plastics, polyethylene and polypropylene are allowed.
5. The above agricultural materials should be purchased from qualified units;
6. When purchasing the above-mentioned agricultural materials, the receipts must be kept for future reference.
[Preparation work before applying for organic certification] includes but is not limited to:
1. Establish a leadership team (organic product leadership team);
2. Learn to write 2 sets of documents (quality manual and operating procedures);
3. The base implements three tests: water quality, soil, and air;
4. The base shall establish four lists: 1) a list of base personnel, 2) a list of agricultural equipment, 3) a list of investment inputs (fertilizers, pesticides, seeds, agricultural films, etc.), and 4) a list of laws and regulations applicable to the certification of the enterprise;
5. The base has established and improved 5 sets of production archive records:
1) Standards and agricultural technology training records;
2) Agricultural records (planting including sowing, fertilization, irrigation, pest and disease control, harvesting, sales, and transportation records);
3) Cleaning records of farm implements and tools;
4) Recall drills and product quality complaint records;
5) Internal inspection records and internal inspection reports;
[Conversion Period Provisions]:
The conversion period for organic cultivation is 24 months from the date of sowing for current year crops and 36 months from the date of harvest for perennial crops.
[Three situations where the conversion period can be exempted]:
1. Do not use soil-grown edible fungi, such as black fungus and shiitake mushrooms;
2Wild plants, such as wild walnuts and wild Chinese medicinal materials.
3. Sprouts, such as mung bean sprouts.
[3 situations where the conversion period can be shortened]:
1Before planting, it was newly reclaimed and abandoned land.
2. Land that can prove that no organic prohibited substances such as chemicals have been used for three consecutive years.
3 Overseas organic planting bases have obtained organic certification from other countries for 4 consecutive years.

Wild Harvesting Base for Organic Products
Agricultural products in their wild state that are listed in the
Wild-harvested products skip the conversion period and receive organic certification directly.
【Preparatory Work Before Applying for Organic Certification】includes but is not limited to:
1. Establish 1 leadership team (organic product leadership group);
2. Compile 2 sets of documents (quality manual, operational procedures);
3. Conduct 2 tests at the base: soil and air;
4. Maintain complete production records:
1) Standards and agricultural technical training records;
2) Farming activity records (harvesting logs, transportation logs);
3) Cleaning records for farm tools and equipment;
4)Recall drills and product quality complaint records;
5)Internal inspection records and internal inspection reports;

Organic product certification (livestock and poultry farming)
Organic product: refers to products that are organically produced and processed for human consumption and animal food.
【Brief introduction to organic livestock and poultry certification knowledge】:
1. They cannot be kept in cages and must be kept in an activity area that complies with organic standards.
2. The food used for feeding must come from organic bases, and the proportion of organic feed must exceed 90%.
3. Conversion period: 12 months for cattle, horses and camels; 6 months for sheep and pigs; 6 months for dairy cows; 10 weeks for meat poultry; 6 weeks for laying fowl.
4. Age requirements for introduction: Beef cattle, horses and camels shall not be more than 6 months old; pigs and sheep shall not be more than 6 weeks old; dairy cattle shall not be more than 4 weeks old and mainly calves fed with full milk; broiler chickens shall not be more than 2 days old, and other poultry shall not be more than 2 weeks old; laying hens shall not be more than 18 weeks old.
5. Lactation period: 3 months for cattle, horses and camels; 45 days for sheep; 40 days for pigs.
6. Requirements for the use of conventional veterinary drugs: Legal vaccines can be administered, but the vaccines must not contain genetically modified organisms. Hormones cannot be fed, and preventive antibiotics are not allowed. Antibiotics can be used for treatment of illness according to veterinary requirements, and the drug withdrawal period is twice that of ordinary livestock and poultry.
[List of application materials for organic livestock and poultry certification] includes but is not limited to:
1. Business license, animal quarantine certificate, and veterinary qualification certificate;
2. Land contract for the stocking site, a layout of the enclosures, and a layout of the stocking area;
3. Drinking water test report.
4. Apply for environmental impact assessment and pollutant discharge permit when necessary.
5. List of heads of departments and equipment.
6. Feed formula list and purchase receipts, vaccine and veterinary drug list and purchase receipts.
[Preparation work before applying for organic certification] includes but is not limited to:
1. Establish a leadership team (organic product leadership team);
2. Learn to write 2 sets of documents (quality manual and operating procedures);
3. The base implements 1 test: aquaculture drinking water environment test;
4. The base shall establish four lists: 1) a list of base personnel, 2) a list of agricultural equipment, 3) a list of investment inputs (feed, veterinary drugs, vaccines, etc.), and 4) a list of laws and regulations applicable to the certification of the enterprise;
5. Establish and improve production archive records:
1) Standards and agricultural technology training records;
2) Agricultural records (including introduction and removal of livestock, feeding, disease control, epidemic prevention, etc.);
3) Cleaning records of equipment and tools;
4) Recall drills and product quality complaint records;
5) Internal inspection records and internal inspection reports;

Organic product certification (aquaculture)
Organic product: refers to products that are organically produced and processed for human consumption and animal food.
Brief introduction to organic aquatic product certification:
1. Conversion period: Non-open water farms must undergo a conversion period of at least 12 months. There is no conversion period for wild fisheries, and organic certificates are issued directly if the water is not polluted and the ecological balance is maintained.
2. Cultivation period: All introduced aquatic organisms should be cultivated organically for at least the last two-thirds of the cultivation period.
3. Feed requirements: The feed for organic aquaculture should be organic and wild. When the quantity or quality of organic or wild feed cannot meet the demand, non-GMO conventional feed can be fed at a maximum of 5% of the total feed.
4. Requirements for medication: After using conventional fishery drugs, the fish can continue to be sold as organic aquatic organisms only after a period of twice the drug-free period has passed.
The list of application materials for organic aquatic product certification includes but is not limited to:
1. Business license and breeding license issued by the fishery department;
2. The lease contract for the water area and the layout map of the water area;
3. Closed waters require environmental protection permits and environmental testing of fishery water quality.
4. List of heads of departments and equipment.
5. List of bait formulas and purchase receipts, list of vaccines and fish medicines and purchase receipts.
6. For wild fishing, submit the certification document of the local competent authority’s consent for wild fishing operations.
[Preparation work before applying for organic certification] includes but is not limited to:
1. Establish a leadership team (organic product leadership team);
2. Learn to write 2 sets of documents (quality manual and operating procedures);
3. The base implements 1 test: fishery water quality;
4. The base shall establish four lists: 1) a list of base personnel, 2) a list of agricultural equipment, 3) a list of investment inputs (bait, fish medicine, etc.), and 4) a list of laws and regulations applicable to the certification of this enterprise;
5. Establish and improve production archive records:
1) Standards and agricultural technology training records;
2) Agricultural records (including feeding, disease control, fishing, etc.);
3) Cleaning records of equipment and tools;
4) Recall drills and product quality complaint records;
5) Internal inspection records and internal inspection reports;

Organic Food:
Organic product: refers to products that are organically produced and processed for human consumption and animal food.
Basic requirements for organic processing projects:
1. The business license and production license must have been valid for at least 3 months; there must be proof of factory property rights, factory map, workshop layout map, and environmental impact assessment permit (if necessary).
3. There must be a drinking water quality test report and a measuring instrument calibration certificate.
4. Name list of heads of each department (must have health certificates).
6. Raw material requirements: ≥95% of the raw materials in the processing project should be certified organic. When organic raw materials are not available, no more than 5% of conventional raw materials can be purchased, and they do not contain genetically modified ingredients.
7. The use of additives, auxiliary agents and disinfectants shall comply with Appendix E of GB/T19630 Organic Product Standard.
8. Processing: Mechanical, freezing, heating, microwave, fumigation and other treatment methods and microbial fermentation processes are recommended; when using extraction, concentration, precipitation and filtration processes, the extraction solvent is limited to water, ethanol, animal and vegetable oils, vinegar, carbon dioxide, nitrogen or carboxylic acid, and other chemical reagents should not be added during the extraction and concentration process. Radiation sterilization is not allowed, and asbestos and other harmful substances filtering materials are not allowed.
9. Use food grade packaging materials and avoid overpackaging.
10. List of raw materials and purchase evidence, list of additives and disinfectants and purchase receipts.
[Preparation work before applying for organic certification] includes but is not limited to:
1. Establish a leadership team (organic product leadership team);
2. Learn to write 2 sets of documents (quality manual and operating procedures);
3. Conduct 1 test (if any): Processing water quality;
IV. List: 1) List of management personnel, 2) List of equipment, 3) List of ingredients, 4) List of laws and regulations applicable to the certification of this enterprise;
5. Establish and improve production archives:
1) Standards and operating technology training records;
2) Record files (including equipment cleaning records, pest control records, feeding records, processing records, inspection records, transportation records, sales records, logo use records, etc.);
3. Recall drills and product quality complaint records;
4) Internal inspection records and internal inspection reports;

【Organic Textiles】:
Organic product: refers to products that are organically produced and processed for human consumption and animal food. Organic textiles refer to products (yarn, thread, silk, cloth and their finished products) made from organic fiber raw materials (bamboo fiber; silk; lint; hemp; kapok).
[Organic textile processing requirements] include but are not limited to:
1. Appropriate methods should be adopted in the textile processing process to reduce the impact on the environment.
2. Substances harmful to the human body and the environment should not be used. The additives used should not contain carcinogenic, teratogenic, mutagenic, or allergenic substances. The oral lethal dose (LD50) for mammals should be greater than 2,000 mg/kg.
3. Substances that are easily bioaccumulative and non-biodegradable should not be used.
4. Energy consumption should be minimized during textile processing, and renewable energy should be used.
5. If separating organic processing from conventional processing in terms of process or equipment will have a significant adverse impact on the environment, the organic and conventional processing processes or equipment may not be separated provided that effective measures are taken to ensure that organic textiles are not contaminated by prohibited substances.
6. Processing units should adopt effective sewage treatment technology to ensure that the concentration of pollutants in the wastewater does not exceed the provisions of GB 4287.
7. An environmental management improvement plan for the processing process should be formulated and implemented.
8. The surfactants used in the cocoon cooking process or wool washing process should be biodegradable.
9. The sizing slurry should be easily degradable or at least 80% can be recycled.
10. In the mercerization process, when sodium hydroxide or other alkaline substances are used, they should be recycled to the maximum extent possible.
11. Textile oil and weaving oil (needle oil) should be biodegradable or plant-extracted.
12. Dyes of plant or mineral origin should be used.
13. Harmful dyes and substances prohibited by GB/T 18885 should not be used
14. It is advisable to use natural printing and dyeing thickeners.
15. It is advisable to use biodegradable softeners.
16. Substances that can form organic halogen compounds in wastewater should not be used to clean printing and dyeing equipment.
17. The heavy metal content in dyes should comply with the indicators in Appendix H Table H.1 of GB/T19630 organic standard.
18. Auxiliary materials in finished products (such as lining, decorations, buttons, zippers, stitching, etc.) should be made of environmentally friendly materials, preferably natural materials.

Introduction to Organic Business Certification (Operation & Trade):
An evaluation activity for distributors and traders regarding the sales of organic products. The certification covers: qualification verification of organic product suppliers, transportation, import/export, warehousing (including cold storage), sales, and full-process traceability verification.
The applicant for organic business certification may distribute organic products from multiple enterprises, including primary agricultural products, fresh produce, frozen products, prepackaged foods, etc.
After obtaining organic business certification, the enterprise can issue an
Requirements for applying for organic business certification include but are not limited to:
1. Possession of a business license and relevant permits, such as food business operation filing.
2. Fixed business premises, storage facilities, and transportation conditions.
3. Stable suppliers of organic products.
4. Professional experience and capability in organic management to prevent contamination at business premises, storage sites, and transportation equipment.
【Preparatory Work Before Applying for Organic Certification】includes but is not limited to:
1. Establish a leadership team (organic product leadership group);
2. Study and compile 2 sets of documents (quality manual, operating procedures);
3. Lists: 1) Management personnel list. 2) Equipment list. 3) Qualified supplier list. 4) List of applicable laws and regulations for the enterprise's certification;
5. Establish comprehensive production records:
1) Standard and operational technical training records;
2) Record files (including equipment cleaning records, pest control records, raw material inspection records, transportation records, sales records, etc.);
3)Recall drills and product quality complaint records;
4)Internal inspection records and internal inspection reports;

【Organic Input Material Evaluation】(Organic Fertilizers, Organic Plant Protection Products):
Enterprises processing organic fertilizers, bio-bacterial fertilizers, and other non-chemical fertilizers, as well as enterprises producing non-chemical plant protection products, can apply for organic input material evaluation.
【Based on Standards】:
GB/T19630 Appendix C《Guidelines for Evaluating Other Input Materials Used in Organic Production》.
GB/T19630 Organic Standard Clause 4.2.7.2: If purchasing organic fertilizers externally, they must be approved by a certification body before use.
【Organic Input Material Evaluation Requirements】(Including but not limited to):
1. Possess a business license and industry permits such as《Fertilizer Registration Certificate》.
2. Have fixed production facilities, which must obtain environmental permits and filings when necessary.
3. Raw materials and processing techniques must comply with GB/T19630 Appendix C《Guidelines for Evaluating Other Input Materials Used in Organic Production》.
4. Stable quality management system and complete production records.
5. Distributors applying for organic input material evaluation may commission qualified enterprises for production and processing.

【Organic catering review】:
The definition of organic catering is that according to the requirements of RB/T 153 standard, it refers to the catering service that provides consumers with food or beverages made or cooked with organic products as raw materials.
According to the RB/T 153-2016 "Organic Catering Evaluation Requirements" standard issued by the National Certification and Accreditation Administration, it is applicable to catering service providers that provide organic catering as the theme, including restaurants, hotel restaurants, snack bars, fast food restaurants, beverage shops, dessert stations, unit canteens, collective dining distribution units and central kitchens.
【Requirements for organic catering】(including but not limited to):
1. At least 95% (by weight) of the raw materials of each organic dish should be products that have obtained GB/T19630 certification and use the China Organic Product Certification Mark.
2. Organic and non-organic versions of the same dish should not exist at the same time.
3. The water quality for cooking and cleaning food contact surfaces should comply with the requirements of GB5749
4. Organic certified condiments such as sugar, soy sauce, vinegar, cooking wine, sauces and spices should be used first.
5. Food additives and adjuvants not listed in the appendix of GB/T 19630, such as colorants, sweeteners and preservatives, should not be used.
6. For catering service providers that mainly sell organic drinks or desserts, the proportion of organic ingredients in their organic drinks or desserts should not be less than 95% (excluding water and salt).
7. Food ingredients and seasonings containing genetically modified ingredients cannot be used.
8. The storage of organic raw materials and auxiliary materials should be managed separately in time and space to prevent mixed contamination. Organic processing and conventional processing should be managed separately in time and space to prevent mixed contamination.
8. Processing operations should comply with the requirements of the "Food Safety Operation Specifications for Catering Services" (State Food and Drug Administration [2011] No. 395).
[Organic catering grade classification]: bronze, silver and gold.
1【Bronze Medal Organic Dining】
1.1. At least 30% of the menu items shall be organic dishes or organic desserts or beverages. For catering services that mainly offer desserts or beverages, at least 30% of the desserts or beverages on the menu shall be organic desserts or beverages.
1.2 When providing staple food, at least one staple food made from organic ingredients should be provided, such as rice and pasta.
2 [Silver Medal Organic Catering]
2.1 At least 60% of the dishes on the menu shall be organic. For catering services that mainly offer desserts or beverages, at least 60% of the desserts or beverages on the menu shall be organic.
2.2 When providing staple foods, at least 50% of the staple foods should be made from organic ingredients.
3.3 At least one beverage that has obtained GB/T19630 certification and uses the China Organic Product Certification Mark or is made from organic ingredients should be provided, such as tea, coffee, and juice.
3【Gold Medal Organic Catering】
3.1 At least 90% of the dishes on the menu shall be organic. For catering services that mainly offer desserts or beverages, at least 90% of the desserts or beverages on the menu shall be organic.
3.2 When providing staple food, it should be made of 100% organic ingredients.
3.3 At least one beverage that has obtained GB/T19630 certification and uses the China Organic Product Certification Mark or is made from organic ingredients, such as tea, coffee, and juice, should be provided.
3.4 Organic cooking oil and seasonings should be used for cooking or preparation.

GAP certification (crops: fields, fruits and vegetables)
Good Agricultural Practice (GAP) is a set of operational standards for agricultural product production, and is an effective means and tool to improve the quality and safety management level of agricultural product production bases. GAP focuses on the control and protection of harmful substances and harmful organisms during the planting, breeding, harvesting, cleaning, packaging, storage and transportation of agricultural products, and ensures the quality and safety of agricultural products. It also pays attention to the protection capabilities of the ecological environment, animal welfare, occupational health and other aspects.
【Why carry out GAP certification】
The implementation of GAP is an internationally accepted and effective measure to strengthen the quality and safety control of agricultural products and food from the source of production, and is a prerequisite for ensuring the quality and safety of agricultural products and food. After obtaining the certification certificate issued by the certification body, the applicant can use the China Good Agricultural Practices certification mark on the retail packaging of certified crops, fruits and vegetables, and other products can use the China Good Agricultural Practices certification mark on the packaging of non-retail products, product promotional materials, and business activities.
Certification Level
Level 1 certification requirements: Level 1 certification should meet the requirements of all applicable Level 1 control points; it should meet at least 95% of the total number of all applicable Level 2 control points.
Level 2 certification requirements: Level 1 should meet at least 95% of the total number of all applicable Level 1 control points, and control points that cause serious hazards to consumers, employees, animal and plant safety, and the environment must meet the requirements.
【GAP certification application conditions】
1. Obtain a business license issued by the competent authority.
2. Have legal land use rights.
3. The certification client has established and implemented documented operating procedures or a good agricultural practice management system in accordance with the standard requirements, and has complete records for at least 3 months before the initial inspection.
4. The product must be included in the Good Agricultural Practices Product Certification Catalogue.
5. The certification client and its related parties have not had any major product quality and safety accidents or any incidents of abuse or fraudulent use of the Good Agricultural Practices certification mark for publicity in the past year.
6. The certification client and its related parties have not had their certification certificates revoked by the certification body within one year.
【GAP certification basis】
GB/T 20014.2 Farm basic control points and compliance specifications;
GB/T 20014.3 Basic control points and compliance specifications for crops;
GB/T 20014.4 Control points and compliance specifications for field crops;
GB/T 20014.5 Control points and compliance specifications for fruits and vegetables;
GB/T 20014.12 Tea control points and conformity specifications;
GB/T 20014.25 Control points and compliance specifications for flowers and ornamental plants;
GB/T 20014.26 Tobacco leaf control points and compliance specifications;
Certification mode: document review + base inspection + product testing + post-certification supervision
Contact information: 18612456966 (Teacher Liu).

GAP certification (livestock and poultry farming)
Good Agricultural Practice (GAP) is a set of operational standards for agricultural product production, and is an effective means and tool to improve the quality and safety management level of agricultural product production bases. GAP focuses on the control and protection of harmful substances and harmful organisms during the planting, breeding, harvesting, cleaning, packaging, storage and transportation of agricultural products, and ensures the quality and safety of agricultural products. It also pays attention to the protection capabilities of the ecological environment, animal welfare, occupational health and other aspects.
Why carry out GAP certification
The implementation of GAP is an internationally accepted and effective measure to strengthen the quality and safety control of agricultural products and food from the source of production, and is a prerequisite for ensuring the quality and safety of agricultural products and food. After obtaining the certification certificate issued by the certification body, the applicant can use the China Good Agricultural Practices certification mark on the retail packaging of certified crops, fruits and vegetables, and other products can use the China Good Agricultural Practices certification mark on the packaging of non-retail products, product promotional materials, and business activities.
Certification Level
Level 1 certification requirements: Level 1 certification should meet the requirements of all applicable Level 1 control points; it should meet at least 95% of the total number of all applicable Level 2 control points.
Level 2 certification requirements: Level 1 should meet at least 95% of the total number of all applicable Level 1 control points, and control points that cause serious hazards to consumers, employees, animal and plant safety, and the environment must meet the requirements.
GAP certification application conditions
1. Obtain a business license issued by a government department and an animal quarantine certificate registered by the competent authority.
2. Have the legal right to use the breeding site.
3. The certification client has established and implemented documented operating procedures or a good agricultural practice management system in accordance with the standard requirements, and has complete records for at least 3 months before the initial inspection.
4. The product must be included in the Good Agricultural Practices Product Certification Catalogue.
5. The certification client and its related parties have not had any major product quality and safety accidents or any incidents of abuse or fraudulent use of the Good Agricultural Practices certification mark for publicity in the past year.
6. The certification client and its related parties have not had their certification certificates revoked by the certification body within one year.
Scope and basis of GAP certification
GB/T 20014.6 Basic control points and compliance specifications for livestock and poultry
GB/T 20014.7 Control points and compliance specifications for cattle and sheep
GB/T 20014.8 Control points and compliance specifications for dairy cows
GB/T 20014.9 Pig control points and compliance specifications
GB/T 20014.10 Poultry control points and compliance specifications
Certification mode: document review + base inspection + product testing + post-certification supervision
Contact information: 18612456966 (Teacher Liu).

GAP Certification (Aquaculture):
Good Agricultural Practice (GAP) is a set of operational standards for agricultural product production, and is an effective means and tool to improve the quality and safety management level of agricultural product production bases. GAP focuses on the control and protection of harmful substances and harmful organisms during the planting, breeding, harvesting, cleaning, packaging, storage and transportation of agricultural products, and ensures the quality and safety of agricultural products. It also pays attention to the protection capabilities of the ecological environment, animal welfare, occupational health and other aspects.
Why carry out GAP certification
The implementation of GAP is an internationally accepted and effective measure to strengthen the quality and safety control of agricultural products and food from the source of production, and is a prerequisite for ensuring the quality and safety of agricultural products and food. After obtaining the certification certificate issued by the certification body, the applicant can use the China Good Agricultural Practices certification mark on the retail packaging of certified crops, fruits and vegetables, and other products can use the China Good Agricultural Practices certification mark on the packaging of non-retail products, product promotional materials, and business activities.
Certification Level
Level 1 certification requirements: Level 1 certification should meet the requirements of all applicable Level 1 control points; it should meet at least 95% of the total number of all applicable Level 2 control points.
Level 2 certification requirements: Level 1 should meet at least 95% of the total number of all applicable Level 1 control points, and control points that cause serious hazards to consumers, employees, animal and plant safety, and the environment must meet the requirements.
GAP certification application conditions
1. Obtain a business license issued by a government department and an animal quarantine certificate registered by the competent authority.
2. Have legal land use rights.
3. The certification client has established and implemented documented operating procedures or a good agricultural practice management system in accordance with the standard requirements, and has complete records for at least 3 months before the initial inspection.
4. The product must be included in the Good Agricultural Practices Product Certification Catalogue.
5. The certification client and its related parties have not had any major product quality and safety accidents or any incidents of abuse or fraudulent use of the Good Agricultural Practices certification mark for publicity in the past year.
6. The certification client and its related parties have not had their certification certificates revoked by the certification body within one year.
Scope and basis of GAP certification
GB/T 20014.13 Basic control points and compliance specifications for aquaculture
GB/T 20014.14 Basic control points and compliance specifications for aquaculture in ponds
GB/T 20014.15 Basic control points and compliance specifications for aquaculture factory farming
GB/T 20014.16 Basic control points and compliance specifications for aquaculture cage culture
GB/T 20014.17 Basic control points and compliance specifications for aquaculture pen culture
GB/T 20014.18 Basic control points and compliance specifications for aquaculture on tidal flats/suspended culture/bottom seeding
Certification mode: document review + base inspection + product testing + post-certification supervision
Contact information: 18612456966 (Teacher Liu).

GAP Certification (Bee)
Good Agricultural Practice (GAP) is a set of operational standards for agricultural product production, and is an effective means and tool to improve the quality and safety management level of agricultural product production bases. GAP focuses on the control and protection of harmful substances and harmful organisms during the planting, breeding, harvesting, cleaning, packaging, storage and transportation of agricultural products, and ensures the quality and safety of agricultural products. It also pays attention to the protection capabilities of the ecological environment, animal welfare, occupational health and other aspects.
Why carry out GAP certification
The implementation of GAP is an internationally accepted and effective measure to strengthen the quality and safety control of agricultural products and food from the source of production, and is a prerequisite for ensuring the quality and safety of agricultural products and food. After obtaining the certification certificate issued by the certification body, the applicant can use the China Good Agricultural Practices certification mark on the retail packaging of certified crops, fruits and vegetables, and other products can use the China Good Agricultural Practices certification mark on the packaging of non-retail products, product promotional materials, and business activities.
Certification Level
Level 1 certification requirements: Level 1 certification should meet the requirements of all applicable Level 1 control points; it should meet at least 95% of the total number of all applicable Level 2 control points.
Level 2 certification requirements: Level 1 should meet at least 95% of the total number of all applicable Level 1 control points, and control points that cause serious hazards to consumers, employees, animal and plant safety, and the environment must meet the requirements.
GAP certification application conditions
1. Obtain a business license issued by a government department and an animal quarantine certificate registered by the competent authority.
2. Have legal land use rights for beekeeping (the base includes nectar-producing crops).
3. The certification client has established and implemented documented operating procedures or a good agricultural practice management system in accordance with the standard requirements, and has complete records for at least 3 months before the initial inspection.
4. The product must be included in the Good Agricultural Practices Product Certification Catalogue.
5. The certification client and its related parties have not had any major product quality and safety accidents or any incidents of abuse or fraudulent use of the Good Agricultural Practices certification mark for publicity in the past year.
6. The certification client and its related parties have not had their certification certificates revoked by the certification body within one year.
GAP certification basis
GB/T 20014.27 Bee control points and compliance specifications
Certification mode: document review + base inspection + product testing + post-certification supervision
Contact information: 18612456966 (Teacher Liu).

GAP (Excerpt from "Good Manufacturing Practice for Chinese Medicinal Materials"
Article 5 Enterprises shall, based on the production characteristics of Chinese medicinal materials, identify the key links that affect the quality of Chinese medicinal materials, conduct quality risk assessments, and formulate effective production management, quality control and preventive measures.
Article 6 Enterprises shall establish an effective supervision and management mechanism for the main production units of the base, realize on-site guidance, supervision and record-keeping of key links; unify the planning of production bases, unify the supply of seeds, seedlings or other breeding materials, unify the management measures for inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides or feed, veterinary drugs, unify the planting or breeding technical procedures, unify the harvesting and production area processing technical procedures, and unify the packaging and storage technical procedures.
Article 7 Enterprises shall be equipped with personnel, facilities, equipment, etc. that are commensurate with the scale of the production base to ensure the smooth implementation of production and quality management measures.
Article 8 Enterprises shall clearly identify the production batches of Chinese medicinal materials and ensure the consistency and traceability of the quality of each batch of Chinese medicinal materials.
Article 9 Enterprises shall establish a quality traceability system for Chinese medicinal materials production to ensure that key links in the entire process, from production sites, seeds and seedlings or other propagation materials, planting and breeding, harvesting and processing at the place of origin, packaging, storage and transportation to shipment, can be traced; enterprises are encouraged to use modern information technology to build traceability systems.
Article 10 Enterprises shall formulate production technical regulations for the following major links in accordance with the requirements of this specification and in combination with production practice and scientific research:
1. Site selection of production base;
(2) Requirements for seeds, seedlings or other propagation materials;
(3) Planting (including ecological planting, wild cultivation and simulated wild cultivation) and breeding;
(iv) harvesting and processing at the place of origin;
(V) Packaging, release, storage and transportation.
Article 11 Enterprises shall formulate quality standards for Chinese medicinal materials, and the standards shall not be lower than the current statutory standards.
(1) Determine the quality control indicators based on the actual production situation, which may include: medicinal material properties, inspection items, physical and chemical identification, extracts, fingerprints or characteristic spectra, indicators or the content of active ingredients; control standards for pesticide residues or veterinary drug residues, heavy metals and harmful elements, mycotoxins and other toxic and harmful substances in medicinal materials;
(ii) When necessary, quality standards for Chinese medicinal materials in the intermediate links such as harvesting, processing and purchasing may be formulated.
Article 12 Enterprises shall formulate standards for seeds, seedlings or other propagation materials of Chinese medicinal materials.

Overview of GLOBALG.A.P. Certification for Good Agricultural Practices:
GLOBALG.A.P. certification is a food safety certification program for agricultural and aquaculture producers. Originally known as EurepGAP, GLOBALG.A.P. is a private organization that establishes voluntary standards for global agricultural product certification. Based on good agricultural practices, the GLOBALG.A.P. food safety standards cover all farm-related processes and are a business-to-business certification. The GLOBALG.A.P. standards apply to 80 countries and assess farms based on three main categories: crops, livestock, and aquaculture.
The Global G.A.P. standards aim to reduce harmful environmental impacts, minimize chemical inputs, and ensure worker health, food safety, and animal welfare. As the source of the entire food supply chain, the safety of agricultural products is increasingly important to consumers. Its control system focuses on the entire process from farm to table.
As the operational manual for good agricultural practices worldwide, Global GAP is based on equal cooperation between agricultural producers and retailers. It establishes trusted partnerships among farmers, investors, companies, retailers, consumers, and the food industry in the supply chain, aiming to create effective certification standards and procedures.
Scope of GLOBALG.A.P Certification
①Crops (including fruits, vegetables, fresh flowers, ornamental plants, field crops, green coffee, and tea leaf standard modules);
②Livestock and poultry;
③Aquaculture;
④Animal feed;
⑤Breeding materials;
Certification model: document review + on-site inspection + product testing + post-certification supervision
Contact: 18612456966 (Mr. Liu).
 GLOBAL.GAP Certification (Global GAP)
GLOBAL.GAP Certification (Global GAP) EU Organic Product Certification
EU Organic Product Certification U.S. Organic Product Certification
U.S. Organic Product Certification Japan Organic Product Certification
Japan Organic Product Certification EU organic assessment (inputs)
EU organic assessment (inputs) BRC Certification
BRC Certification FSSC22000 Certification
FSSC22000 Certification IFS Certification
IFS Certification HALAL certification (Habits of Muslim Life and Diet)
HALAL certification (Habits of Muslim Life and Diet) BAP (Aquaculture Practice)
BAP (Aquaculture Practice) MSC Certification (Aquatic Products)
MSC Certification (Aquatic Products) GMP Certificate Counseling (CAC International Codex Alimentarius Commission Standards)
GMP Certificate Counseling (CAC International Codex Alimentarius Commission Standards) FDA Food Registration Counseling
FDA Food Registration Counseling

GLOBAL.GAP Certification (Global Good Agricultural Practice Certification) Introduction:
Global Good Agricultural Practice Certification (GLOBALGAP) is established as the primary reference for good agricultural operation standards within the global market scope. The GLOBALGAP certification standards cover the entire process from planting to harvesting of certified products. As the source of the entire food supply chain, the safety of agricultural products has become an increasing concern for consumers. To address food safety issues at the source, major European supermarket groups controlling the retail market pioneered the development of GAP (Good Agricultural Practice) control system standards for planting/breeding processes.
GLOBALGAP Certification Scope:
1. Crops (including fruits and vegetables - field crops - flowers and ornamental plants - hops/beer flowers - tea leaves - plant propagation materials);
2. Livestock (including cattle and sheep, dairy cattle, pigs, poultry modules);
3. Aquaculture (including salmon module);
4. Animal feed;
What are the main commitments of GLOBAL G.A.P.?
1. Food safety and traceability;
2. Environmental protection (including biodiversity);
3. Employee health, safety and welfare;
4. Animal welfare;
5. Integrated Crop Management (ICM);
6. Integrated Pest Control (IPC);
7. Quality Management System (QMS);
8. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP).

1. What is SRS equivalent EU organic product certification
SRS EU equivalent organic standard is equivalent to the provisions of Council Regulation (EC) No. 834/2007 of June 28, 2007 and Commission Regulation (EC) No. 889/2008 of September 5, 2008 and the requirements of relevant equivalent standards. It is the act of inspecting the product range, process range and site range of an enterprise and issuing organic certificates.
2. Which companies need to apply for SRS equivalent EU organic product certification
Companies that need to export "organic" products to the EU market or markets in countries with equivalent EU standards
3. Which products can apply for SRS equivalent EU organic product certification
The following agricultural products that have been put into or are planned to be put into the EU market can apply for EU organic product certification:
(1) Live or unprocessed agricultural products
(2) Processed agricultural products to be used as food
(3) Feed
(4) Yeast used as food or feed
(Items that cannot be applied for: soft-shelled turtles, wild animal products from fishing and hunting, etc.; processed products not for human food (except feed), such as lint, etc.;)
4. How to prepare for EU organic product certification
(1) Select a base or processing plant whose environment meets EU standards;
(2) Documentation: Establish a series of management system documents in accordance with standard requirements and maintain effective operation;
(3) Operationally: Conduct organic production or processing activities in accordance with the standards and keep records;
5. How long does it take to get the certification results?
Generally, the certification time can be divided into three parts: the time before the on-site inspection + the time from the inspection to the certification decision + the time for the enterprise to make rectification = the time to obtain the certificate. The time before the on-site inspection mainly depends on the time the enterprise takes to prepare the materials, which means that this part of the time is controlled by the enterprise itself. It takes 30 days from the on-site inspection to the issuance of the certification decision. The time for the enterprise to make rectification also depends on the speed of the enterprise's rectification, which is still controlled by the enterprise itself. The entire process from applying for certification to obtaining the certificate can be completed in 2 to 3 months if the enterprise actively cooperates.
6. Entering the EU market and using EU organic product labels and logos
The graphic and color requirements of the EU organic product certification mark are shown in the figure below. Please follow the following principles for printing:
a. Dimensions: The height: width of the EU organic logo is 1:1.5, and the logo must not be tilted, flipped or changed; at least 9mm high (6mm on small packaging materials) and 13.5mm wide.
b. Color: The color logo is composed of bright green and pure white, Pantone green color card 376 or four-color color card CMYK: 50/0/100/0

7. Validity period of organic certification
Generally speaking, organic certification certificates are valid for 12 months, and must be resubmitted and inspected three months in advance each year.
8. Is there a conversion period for EU organic products?
Generally speaking, the conversion period varies depending on the growth cycle of crops or farmed animals. The inspector will make a specific determination based on the on-site situation.

1. What is the US standard (NOP) organic product certification
The act of inspecting a company’s product, process, and site scope and issuing an organic certificate in accordance with the requirements of the Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA), the USDA’s organic regulations (7 CFR Part 205), and the NOP Handbook.
2. Which companies need to apply for US (NOP) organic product certification?
Companies that need to export "organic" products to the U.S. market or markets in countries with equivalent U.S. standards
3. Which products can apply for US standard (NOP) organic product certification
Applicable to products that are produced (planted, collected from wild plants), processed, and sold. (Products that cannot be applied for are aquatic animal products)
4. How to prepare for US standard (NOP) organic product certification
(1) Select a base or processing plant whose environment meets the requirements of US standards (NOP);
(2) Documentation: Establish a series of management system documents in accordance with the standard requirements and maintain effective operation;
(3) Operationally: Conduct organic production or processing activities in accordance with the standards;
5. Time to obtain the US standard (NOP) organic product certification results
Generally, the certification time can be divided into three parts: the time before the on-site inspection + the time from the inspection to the certification decision + the time for the enterprise to make rectification = the time to obtain the certificate. The time before the on-site inspection mainly depends on the time the enterprise takes to prepare the materials, which means that this part of the time is controlled by the enterprise itself. It takes 30 days from the on-site inspection to the issuance of the certification decision: the time for the enterprise to make rectification also depends on the speed of the enterprise's rectification, which is still controlled by the enterprise itself. The entire process from applying for certification to obtaining the certificate can be completed in 2 to 3 months with active cooperation.
6. Organic products entering the U.S. market and the use of U.S. organic logos and labels
If the USDA organic seal is used, it must be printed in one of two ways:
(1) Completely black and white or;
(2) green and white with a brown outer ring;

The colors green and brown are specified, no other colors are permitted, and both versions of the icon can be downloaded from the National Organic Program (NOP) website. The certifying agency's logo may not appear more prominently than the USDA logo.
7. Validity period of the certificate for US standard (NOP) organic product certification
Generally speaking, organic certification certificates are valid for 12 months, and must be resubmitted and inspected three months in advance each year.
8. Is there a conversion period for US standard (NOP) organic product certification?
Generally speaking, the conversion period varies depending on the growth cycle of crops or farmed animals. The inspector will make a specific determination based on the on-site situation.

1. What is Japan Agricultural Standard (JAS) Organic Product Certification
In accordance with the requirements of Japan's Organic Products Law, it involves inspecting the product scope, process scope, and site scope of enterprises, and issuing organic certificates.
2. Which enterprises need to apply for Japan Agricultural Standard (JAS) Organic Product Certification
Enterprises that need to export "organic" products to the Japanese market or equivalent markets with Japanese standards.
3. Which products can apply for Japan Agricultural Standard (JAS) Organic Product Certification
Applicable to products for production (cultivation, edible fungi, collection, etc.), processing, and repackaging. (Non-applicable scope includes: plants or processed products not for human consumption, livestock, and aquatic animal products, etc.)
4. How to prepare for Japan Agricultural Standard (JAS) Organic Product Certification
(1) Select a base or processing plant that meets the requirements of Japan Agricultural Standard (JAS).
(2) Documentation: Establish a series of management system documents according to standard requirements and maintain effective operation.
(3) Operation: Conduct organic production or processing activities in accordance with standard requirements.
5. Entering the Japanese market: Japan Agricultural Standard (JAS) Organic Product Labels and Tags
The shape and color requirements of Japan's organic product certification logo are as shown in the figure. Please follow the following principles when printing:
The height of the JAS logo (excluding the name of the certification body) must be at least 5 millimeters, and the shape and proportion cannot be altered.
6. Validity period of Japan Agricultural Standard (JAS) Organic Product Certification
Generally, the validity period of organic certification is 12 months. Applications must be resubmitted three months in advance each year, and inspections must be conducted.
7. Is there a conversion period for Japan Agricultural Standard (JAS) Organic Product Certification?
Generally, the conversion period varies depending on the growth cycle of crops or livestock. The inspector will determine the specific period based on the on-site situation.

Organic Input Material Evaluation:
Organic input materials refer to fertilizers and plant protection products permitted for use in organic farm bases. According to EU organic standards, commercial fertilizers used in organic farms must be evaluated and certified by an organic certification body, with an evaluation certificate issued.
Certification evaluation scope: organic fertilizers, processed farmyard manure, biological bacterial fertilizers, and other fertilizers not processed using transgenic technology or chemical raw materials.
List of Application Materials:
1. Business license and fertilizer registration certificate;
2. List of production raw materials and production process documentation;
3. Environmental assessment procedures;
4. Current year's metrology verification certificate and product testing report;
5. Complete system documentation and production records;
6. No adverse records in environmental protection, safety, taxation, or credit aspects.

BRC Overview
In 1998, the British Retail Consortium (BRC) industry requirements led to the establishment of the BRC Food Technical Standard (BRC Food Technical Standard) to assess the safety of food products from retailers' own brands. The BRC certification has become an internationally recognized food safety standard, not only used to evaluate the supply chain of retailers but also to help many international companies establish their own supply chain evaluation systems and brand product production standards.
Significance of Certification:
Initially, the standard was required for food exported from the UK and other European and international markets. However, as its name suggests, the global standard has become the best practice for supply chains across multiple industries, not only for evaluating retailers' brand products and food production but also for product certification. After passing the audit, the certification body will issue a BRC certificate. Many European and global retailers (such as Walmart) consider BRC certification as a basic requirement when selecting suppliers, making it a crucial certification for entering the international market.
BRC Certification Product Scope:
Food (Food);
Consumer Goods (Consumer Product);
Food Packaging Materials (Food Packaging material);
Storage and Distribution (Storage and Distribution);
Non-GMO Foods (Non GM Foods);
Certificate Levels:
Divided into A-B-C-D four levels, D level does not issue a certificate, A-B is valid for 1 year, C is valid for 6 months.
BRC Standard Requirements:
Food safety management system;
HACCP principles;
Hygiene requirements for personnel and facilities;
Control of hazardous products;
Control of good operating practices and verification methods;
Traceability in the food supply chain;
Continuous improvement of the system.

Introduction to Food Safety System Certification (FSSC22000)
Food Safety System Certification (FSSC) 22000 was created for food manufacturers and integrates the ISO22000:2005 food safety standard and the Food Safety Public Available Specification (PAS) 220. It was developed by a foundation based in the Netherlands for food safety certification and supported by the EU Food and Beverage Industry Alliance. FSSC22000 has been approved by the Global Food Safety Initiative and encouraged to promote its implementation. The certificate will be recognized under the standards of ISO22003 and ISO Guide 65 (product certification), providing organizations with a complete food safety management system.
FSSC 22000 is a global, auditable food safety management system standard that combines Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), HACCP and other management system requirements. FSSC 22000 provides a globally recognized standard for food companies to demonstrate that they have established a comprehensive management system and fully meet customer and industry regulatory requirements for food safety. This standard is designed to cover all processes in the food supply chain, whether directly or indirectly related to the final product. It provides a unified food safety management approach for companies in the food supply chain and is easy to be accepted, implemented and audited by organizations at different stages of the food supply chain.
FSSC22000 application scope:
1. Perishable animal products, including slaughter (e.g. canned meat, poultry, eggs, dairy products, fish products)
2. Perishable vegetable products (e.g. juice, preserves, canned vegetables, pickles)
3. Products with a long shelf life (e.g. biscuits, snacks, oil, drinking water, beverages, flour, sugar, salt)
4. (Biological) chemical products that need to be added during the food manufacturing process (e.g. additives, vitamins and biological additives) excluding process technology and process aids
5. Feed products (animal feed, fish feed, etc.).

IFS-FOOD International Featured Standard for European Retail
International Featured Standard – Food Safety (IFS-FOOD)
The International Featured Standard (IFS), jointly issued by Europe's two major retail organizations, France's FCD and Germany's HDE, requires food suppliers entering the EU retail market to obtain IFS certification.
The IFS standard provides clear management specifications and requirements for food suppliers to large retailers, particularly for "private label" food manufacturers. Through the implementation and certification process of the IFS standard, manufacturers can clearly identify, control, and reduce potential hazards in food production, ensuring product safety and facilitating entry into the European market.
IFS Standard Requirements:
Food safety management system;
HACCP principles;
Hygiene requirements for personnel and equipment;
Control of perishable products;
Scope and verification methods for good operating practices;
Traceability in the food supply chain;
Continuous improvement of the system;

Halal Definition:
The word Halal means: "permitted, acknowledged, approved, ratified, consented, legally permitted, legal, lawful or legitimate". When used in relation to food or drink, in either form, it means permitted and fit for Muslim consumption.
To be considered Halal, a food or drink must be in accordance with Islamic dietary laws, as detailed in the Quran, the Hadith (sayings) of the Prophet Muhammad and his Shariah (traditions), and in the Fiqh (teachings) of Islamic jurists: "Hanafi, Sahfi'i, Malki, Hanbali, etc." Other regulations come from Ijma' (collective scholars) and Qiyas (similar) Islamic scholars.
The Halal Certification Authority (HCA) certifies products that meet the above conditions, so certified products can be accepted by all Muslims.
Halal Products:
A product is considered Halal if it, in whole and in part, complies with the following requirements:
1. Does not contain any substance or ingredient obtained or extracted from Haram animals or ingredients.
2. Processing, production, manufacturing and/or storage using instruments, equipment and/or machines that have been purified according to Islamic teachings.
3. It must not come into contact with, come into contact with, or be near Haram (non-lawful food according to Islamic law) substances during preparation, manufacturing, production, processing and/or storage.
What are the raw materials for processed foods that meet HALAL requirements?
In principle, the following products can be considered halal:
1. Milk (or goat milk, camel milk);
2. Honey;
3. Fish;
4. Plants (non-intoxicating);
5. Fresh or frozen vegetables;
6. Fresh fruits and dried fruits;
7. Beans and nuts such as peanuts, cashews, hazelnuts, walnuts, etc.
8. Cereals, such as wheat, rice, rye, oats, etc.;
9. Animals such as cattle, sheep, deer, elk, chickens, ducks, game birds, etc. are also halal, but they must be slaughtered in a manner that complies with Islamic law before they can be eaten (or used for other purposes).
What are the raw materials of processed foods that do not meet HALAL requirements?
A product that comes in contact with or contains in whole or in part any of the following is considered a Haram product ("not permitted, recognized, approved, approved, consented, legally permitted, illegal, unlawful or improper.").
1. Animals that are not slaughtered in a halal manner
2. Pigs, dogs, donkeys or carnivores
3. Animals killed by slaughter, blow to the head (e.g. clubbing), falling, natural death (carrion), congestion, or attack by other animals
4. Animals with prominent canine teeth such as monkeys, cats and lions.
5. Amphibians, such as frogs and crocodiles.
6. Unwelcome insects such as worms, flies and cockroaches.
7. Birds that hunt with their claws, such as owls and hawks.
8. Alcohol, harmful substances, poisonous and intoxicating plants or beverages.
9. Blood
Halal Certified Product Production Guide
1. Carry out equipment cleaning under supervision.
2. Raw material and product storage rooms and preparation areas should be isolated and differentiated.
3. Storage and processing of halal products should be carried out under supervision.
4. Halal and non-halal products should not be processed in the same equipment at the same time.
5. Raw, unprocessed seafood, vegetables and fruit ingredients do not have to be Halal certified and can be obtained from any supplier.
6. Raw materials, except as mentioned in clause (5), should be procured from Halal approved suppliers and kept segregated in the storage room from other ingredients which are not acceptable for non-Halal products.
7. Any product, ingredient or finished product that is not approved or certified cannot be used in the preparation of halal products.
8. Halal products that come into contact with non-halal products during processing will not be considered, labeled or sold as Halal and should be treated as ordinary products.

【BAP Certification for Aquaculture Standards Introduction】:
BAP was established by the Global Seafood Alliance (GSA) and published in 2002. The Best Aquaculture Practices (BAP) certification is the world's most comprehensive third-party aquaculture certification solution, with standards covering the entire production chain including farms, processing plants, hatcheries, and feed mills.
Currently, BAP has issued 6 certification standards based on production models, certifying 99% of aquatic species—such as crabs, shrimp, and fish—ensuring consumer dining safety.
【Benefits of Obtaining BAP Certification】:
1. Strengthen your position in existing markets and expand into new ones;
2. Enhance credibility within the industry and among consumers to increase market value;
3. Align with industry best practices to gain a competitive edge (e.g., through improved feed efficiency and disease control);
4. Many global retailers and foodservice companies publicly commit to sourcing seafood from BAP-certified suppliers.
【Consultation and Certification Process】:
1. Project consultants provide guidance and training;
2. Prepare application materials, including survey questionnaires;
4. Implement the system and establish record-keeping;
5. Pre-audit preparation;
6. On-site audit;
7. Non-conformity corrective actions;
8. Obtain certification.

[MSC Seafood Certification Introduction]:
Many people on Earth rely on fish for survival, but in recent years, 70-80% of fishery resources are being overexploited, with resources either depleted or in the process of recovery. Overfishing has become one of the increasingly severe global environmental issues. In 1996, Unilever and the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) jointly initiated the establishment of the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), forming working groups in major fishery regions worldwide to develop the "Standards for Sustainable Fisheries and Good Management Practices." The MSC was officially founded on March 1, 2000, with key founding members including major retailers, manufacturers, and food service providers from Europe and America. The MSC is an independent, non-profit organization with permanent offices in London, Seattle, and Sydney.
The MSC seafood standard is based on three core principles:
1. Sustainable fishing;
2. Impact of fisheries on marine ecosystems;
3. Effective fisheries management;
[Significance of MSC Certification]:
MSC-certified seafood products can carry the MSC certification label, which signifies: "This product comes from fisheries that meet the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) environmental standards and comply with requirements for good management and sustainable fishing." This certification label applies to seafood products and their supply chains, including storage, processing, sales, and transportation, proving that the product originates from fisheries with optimal fishing practices.

What is GMP certification
GMP Good Manufacturing Practice, also known as CGMP, C stands for Current, which means good on-site production practice.
GMP regulates enterprises in different industries from aspects such as factory site selection, factory buildings, equipment, facilities, personnel, raw materials and auxiliary materials, production/operation processes, inspection, storage, transportation, complaints, recalls, product information, and training, to help enterprises form good production and operation standards to ensure product quality, safety, and suitability for consumption.
In the food and cosmetics industries, GMP is a voluntary certification for companies.
Good Manufacturing Practice for Dairy Products
In 2008, the Shijiazhuang Sanlu milk powder food safety incident broke out, which aroused great concern of the whole society about food safety. In order to actively respond to the "milk powder incident", promote the healthy development of China's dairy industry, and ensure the quality and safety of dairy products and other foods, the State Council and relevant departments organized the compilation of the "Dairy Quality and Safety Supervision and Management Regulations", which was promulgated on October 9, 2008. On November 19, 2008, the National Development and Reform Commission and 13 other ministries and commissions jointly issued the "Outline of the Dairy Industry Rectification and Revitalization Plan". In both documents, it is mentioned that food safety can be further improved by carrying out GMP and HACCP certification for dairy-related enterprises.
GMP+ certification for the feed industry
With the development of the breeding industry, there are more and more food safety issues related to the feed industry. For example, abuse of antibiotics, clenbuterol, Sudan red and melamine. People are paying more and more attention to the control of the feed industry at the front end of the food chain. The GMP certification of the feed industry has been highly valued by developed countries and regions such as the United States and the European Union. Some well-known Chinese companies have joined the ranks of GMP certification in the feed industry. GMP certification in the feed industry has become a useful tool for enterprises to standardize production/operation, prove their capabilities and enhance public confidence.
Benefits of GMP Certification
· Prove the company's management capabilities in product quality and safety assurance
· Help employees develop good production/operation habits
Reduce the company's risk in product quality and safety
· Timely discover production and management problems to reduce costs
Better understand and meet the requirements of relevant laws and regulations
Enhance international credibility and public image
Increase customers’ long-term confidence in the company
GMP certification process:
1. Fill in the application form and enterprise information questionnaire; submit copies of business license, organization code certificate and other necessary qualification certificates such as licenses; submit the required management documents, enterprise plant map and floor plan;
2. Sign the certification contract;
3. Implement the first phase of the audit, namely on-site assessment and document review;
4. After the problems found are improved (if any), the second stage of audit will be implemented;
5. Supervision and audit;
6. Review (the certificate is valid for 3 years).

GRAS/NDI Declaration
"GRAS" is the acronym for Generally Recognized As Safe in English. According to Chapters 201(s) and 409 of the U.S. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, any substance intentionally added to food is considered a food additive and requires mandatory FDA premarket approval, with a few exceptions. GRAS is one such exception, where substances functionally qualify as food additives but are exempt from the lengthy and rigorous FDA approval process due to their "high safety profile."
For food companies, botanical enterprises, and traditional Chinese medicine manufacturers, entering the mainstream U.S. health product market through NDI registration is a more economical and expedient approach.
The FDA's approval process for GRAS and NDI is highly complex and specialized. The approval rate is low, so Chinese companies seeking GRAS or NDI certification are advised to work with expert agencies that have professional expertise and background.

In the certification of selenium-enriched products in livestock and aquaculture categories, the primary method involves animals consuming selenium-enriched feed to absorb selenium elements, ensuring that meat products or eggs meet the standard range for selenium content. The feed may consist of natural selenium-rich plants or include additives like selenized yeast. The selenium-enriched standard is achieved through animal digestion and absorption.
Certification scope includes: live animals such as pigs, cattle, sheep, fish, and poultry eggs; animal products like meat.
Requirements for selenium-enriched product certification:
1. Breeding enterprises must provide: business license, animal epidemic prevention qualification certificate (for livestock), aquaculture license (for aquaculture), and documentation proving the source of selenium-enriched feed.
2. Processing enterprises must provide: business license, industry permit, and documentation proving the source of selenium-enriched raw materials.
3. Other materials required to meet certification standards.



Concept of Cage-Free Chicken Certification:
Raising chickens without using cages, adopting free-range or mountain-range farming methods. Chickens and eggs produced through cage-free farming, with proper exercise and scientific feeding, exhibit superior product quality and taste compared to caged poultry products.
Significance of Cage-Free Chicken Implementation:
Cage-free chicken certification sets requirements for social responsibility, food safety, sustainable environmental protection, animal health and welfare, and traceability. During the farming process, it emphasizes scientific management, resource conservation, animal health protection, and creating a benign ecological environment. It balances the relationship between farming production and environmental protection, ultimately achieving healthy farming production and providing humans with healthy, safe, and nutritious poultry products.
Products certified as cage-free can enhance brand recognition, thereby increasing revenue for certified organizations.


Green Product Certification:
What is the purpose of Green Product Certification?
CAIQ Green Product Certification ensures the full traceability and quality safety of your green products, achieving corporate sustainability.
What are the key points of Green Product Certification?
Green raw materials must come from the company's own green supply chain (forest) and CAIQ Green Product Certification.
Analyze and identify potential hazards and risks in the production process, taking appropriate preventive measures.
Design a reasonable production process to ensure product quality and safety.
Achieve the full traceability of green products: "green (forest) - production - export - import - reproduction - sales - consumption".
Demonstrate the carbon content in green products to consumers, enabling carbon trading and fulfilling local production and consumption responsibilities.
How to obtain the Green Product Certification mark?
Apply through the certification body Ecocert to implement the CAIQ Green Product Certification audit, ensuring your activities comply with the relevant requirements of Green Product Certification.
All products with the Green Product Certification mark must pass the certification body's audit and obtain certification.
After obtaining CAIQ Green Product Certification, companies must submit samples to the certification body for verification before using the CAIQ Green Product Certification mark.
After obtaining CAIQ Green Product Certification, companies can apply to the China Certification and Accreditation Association for the CAIQ Green Label.
Which products are Green Product Certification applicable to?
Green Product Certification is applicable to green and related products, including various green products, frozen green products, green by-products, green canned products, convenient green products, green mooncakes, and green health products.
For more details, please consult Ecocert.

【Definition of Ripened Honey】:
Ripened honey is a natural sweet substance produced by honeybees through the collection of floral nectar or secretions from living plants, or excretions of plant-sucking insects, which are then stored in honeycombs and transformed through the addition of special enzymes, ripening, and dehydration processes.
【Floral Honey】:Honey derived from plant flowers.
【Honeydew Honey】:Honey primarily sourced from bees collecting excretions of plant-sucking insects or secretions from living plants.
Description: The main components of honey are various sugars, primarily glucose and fructose, along with other substances such as organic acids, enzymes, and solid particles brought back by bees during collection. Honey color ranges from nearly colorless to dark brown; it can be liquid, viscous, partially crystallized, or fully crystallized; its form may be liquid, gelatinous, or crystallized; and its aroma varies depending on the nectar source plant.
【Site Selection Requirements for Ripened Honey Beekeeping】:
Apiaries should be established in areas suitable for bee colony proliferation and production. Apiary sites must be far from dust, residential areas, busy traffic routes, chemical plants, livestock farms, and open toilets, with high terrain, sheltered from wind, facing the sun, free from harmful gases, smoke, and other pollutants, with good drainage and suitable microclimate conditions. The distance between apiaries should be no less than 3 km. Within a 5 km radius of the apiary, there should be no pesticide factories, pesticide warehouses, or food factories using honey or sugar as raw materials. Apiaries should have convenient access to good water sources for honey collection.
【Nectar Source (Foraging Area) Requirements for Ripened Honey】:
There should be sufficient nectar source plants to support bee colony proliferation and honey production. Within a 3 km radius of the apiary, there should be abundant nectar source plants. Fixed apiaries should have at least one main nectar source plant and multiple auxiliary nectar source plants with staggered flowering periods nearby, ensuring a continuous flowering period of at least 10 days. Beekeepers should avoid placing hives in areas where nectar source plants are being sprayed with pesticides.
【Processing Workshop Requirements for Ripened Honey】:
Must comply with the requirements of GB14881 "National Food Safety Standard - General Hygienic Specifications for Food Production."

What is animal welfare?
Animal welfare refers specifically to the living conditions of animals. It is scientifically proven that if animals are healthy, comfortable, well-nourished, safe, able to freely express their nature and are not threatened by pain, fear and stress, then animal welfare requirements are met. A high level of animal welfare requires disease immunity and veterinary treatment, appropriate housing, management, nutrition, humane treatment and humane slaughter.
【Five Principles of Animal Welfare】
Physiological welfare, that is, no worries about hunger and thirst;
Environmental welfare, that is, ensuring that animals have adequate housing;
Health and welfare, mainly to reduce animal injuries and diseases;
Behavioral welfare, animals should be guaranteed the freedom to express their nature;
Psychological benefits, i.e. reducing the animals’ fear and anxiety.
【What is Animal Welfare Certification? 】
Animal welfare certification is based on the five internationally recognized animal welfare principles. It starts from the core production factor of livestock and poultry farming, namely the animals themselves, and is based on the concept of treating animals scientifically, reducing animal pain and stress reactions, providing animals with a suitable growth environment and nutrition, and improving animal survival and health levels. It creates a benign ecological environment in the breeding process, coordinates the relationship between breeding production and environmental protection, and ultimately achieves healthy breeding production, providing humans with healthy, safe and nutritious breeding products.
【Benefits of Animal Welfare Assessment】
Improve animal health levels, enhance product quality and safety, form a healthy livestock and poultry product production, processing, procurement and sales industry chain, and promote high-quality and sustainable development of the industry.
While ensuring economic benefits, we fulfill our social responsibilities and improve our market competitiveness.

With the development of the breeding industry, food safety issues related to the feed industry have become increasingly prominent, such as the misuse of antibiotics, lean meat powder, Sudan red, and trichlorfon. There is growing public concern over the control of the feed sector at the front end of the food supply chain. GMP certification in the feed industry has gained significant attention from developed countries and regions like the U.S. and the EU. Several renowned Chinese companies have joined the ranks of GMP-certified feed producers. GMP certification has become a vital tool for standardizing production/operations, demonstrating capability, and enhancing public trust in the feed industry.
By conducting inspections on key aspects such as the origin of pet food ingredients, vulnerability assessments of raw materials, supplier evaluations, material acceptance and quality testing, warehouse management, and traceability systems, we ensure the safety and authenticity of pet food ingredient sources. Additionally, through comprehensive checks on pet food factories—including personnel management, equipment maintenance, additive usage, foreign contaminant control, cross-contamination prevention, pest management, critical process control, finished product warehousing, sanitation management, logistics, and final inspection—we ultimately achieve ingredient integrity and supply chain traceability.
Key Inspection Points:
Social Responsibility & Integrity Program
Environmental Friendliness
Basic Management
Raw Material Supply Chain Management
Production Process Management
Finished Product Warehousing & Logistics Management
Food Safety & Protection
Label Management
Traceability & Crisis Management
Anti-Fraud Management
Implementation Significance:
Transparent Labeling of Pet Food Ingredients
Ensuring Pet Food Safety
"Source-to-Sales Full-Chain Traceability"

The food safety management system standard ISO 22000:2018 is a preventive system for controlling hazards based on prerequisite programs (PRPs) and HACCP plans. It is currently the most authoritative food safety quality management system standard in the world.
Development of Food Safety Management System (HACCP) Requirements
The HACCP system first appeared in the 1960s. The Pillsbury Company in the United States took the lead in applying the HACCP concept when it provided food for the US space program. In 1985, the National Academy of Sciences of the United States proposed that the HACCP system should be adopted by all law enforcement agencies and should be mandatory for food processors. In December 1995, the HACCP regulations were announced. The first two regulations to be implemented in the United States were the Aquatic Products Management Regulations and the Meat and Poultry Management Regulations implemented in January 1998. The scope of implementation includes American products and foreign imported products. Thus, the seven principles of the HACCP plan were gradually formed.
In China, HACCP certification and food safety management system certification have gradually become two independent certification systems. The National Certification and Accreditation Administration of China announced the "Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points HACCP Management System Certification Management Regulations for Food Production Enterprises" to standardize the establishment, implementation and verification of relevant HACCP management systems, stipulate self-implementation, and make it a prerequisite for the review of food quality and safety marks. In 2009, the national standard GB/T27341 for HACCP certification was issued and implemented, and a complete HACCP certification system was gradually formed.
At the same time, in July 2002, the National Certification and Accreditation Administration, the Ministry of Science and Technology, the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, the Ministry of Health, and the Ministry of Agriculture launched research on key food safety technologies, and as a major national science and technology project in the 15th Five-Year Plan, it has now adopted the international standard ISO22000 "Food Safety Management System Requirements for Organizations in the Whole Food Chain" as a national standard, and in 2006, the National Standardization Administration approved the release of the national standard "Food Safety Management System Requirements for Organizations in the Whole Food Chain" GB/T22000-2006. In March 2010, the National Certification and Accreditation Administration issued and implemented the "Food Safety Management System Certification Implementation Rules", which detailed the requirements for food safety management system certification. In June 2018, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) released the newly formulated ISO22000:2018 standard.
Special note: This standard also applies to other organizations indirectly involved in the food chain, including but not limited to suppliers of equipment, cleaning agents, packaging materials and other food contact materials.
Food safety management system certification basis: GB/T 22000 "Food safety management system requirements for various organizations in the food chain" / ISO 22000 Food safety management systems: Requirements for any organizations in the food chain
The validity period of the food safety management system certification certificate is 3 years. The certified organization shall accept the follow-up supervision and audit by the certification body during the validity period of the certificate. The longest time interval between supervision and audit shall not exceed 12 months. Seasonal products shall be supervised during the production season. If necessary, the supervision and audit shall verify the safety of the product. To ensure the continuous validity of the certification, the certified organization shall apply for re-certification three months before the expiration of the certificate.
The conditions that an enterprise must meet for ISO22000 certification (including but not limited to):
1. Must have production license (SC), business license and other qualification certificates;
2. Safety of water (ice) in contact with food or the surface of food contact objects;
3. Cleanliness of food contact surfaces (including equipment, gloves, and work clothes);
4. Prevent cross contamination;
5. Washing and disinfection of hands, maintenance and sanitation of toilet facilities;
6. Toxic chemicals should be clearly marked and placed in a dedicated area for storage and use;
7. Health and hygiene control of employees;
8. Prevention and control of diseases and pests.
9. Food pipes used in the workshop must be food grade (usually stainless steel pipes) and must not be dragged on the ground;
10. Explosion-proof lamps should be installed in the workshop;
11. Exhaust fans should be equipped with filters;
12. Work clothes in the disinfection room should be hung out for disinfection, and there should be a door to isolate the air;
13. Methods for waterproofing the workshop from condensation dripping: The height should be sufficient, exhaust fans should be installed to exhaust air frequently, wooden, bamboo and plaster ceilings should not be used, and refrigerated water pipes should not pass directly over food;
14. The filling workshop and the packaging workshop should be strictly separated, that is, the packaging room should be independent;
15. The hand washing and disinfection equipment should be equipped with a non-manual faucet and have hot and cold water supply (for non-manual faucets, as long as there is one in the hand washing and disinfection room, the rest is not required), and a hand drying device (such as a hand dryer, disposable towels or paper towels, etc.);
16. After disinfection, empty bottles should be promptly transferred to the bottling workshop for bottling to prevent re-contamination.
List of required application materials (including but not limited to):
1. Business license, production license and detail page;
2. Application form, questionnaire, and certification contract;
3. Product implementation standards, production process documents, plant layout diagram, equipment layout diagram, pest control layout diagram, and process flow chart.
4. Calibration certificate for measuring instruments, registration certificate for special equipment, and calibration certificate for special equipment.
5. Product testing report and water quality testing report (more than 36 items).
6. Personnel health certificate, special job training certificate (such as electrician, forklift operator, crane operator)
7. Procedure documents, hazard analysis and control plan, and management manual.
8. List of production and testing equipment.
9. List of laws and regulations.
Certification mode: document review + factory audit + post-certification supervision

HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) is a scientific and systematic method for hazard identification, evaluation and control. It is applied in the process from the production of primary products to the consumption of final products. Through hazard analysis, the possibility and severity of hazards are determined, and specific hazards and their control measures are identified and evaluated, so as to prevent the occurrence of food safety hazards and ensure food safety.
The concept of HACCP originated in the United States in the 20th century. The HACCP principle was applied in the development of space food and played a very good role, and was quickly promoted and applied throughout the world.
HACCP mainly includes 7 basic principles:
Principle 1: Conduct a hazard analysis.
Principle 2: Identify critical control points.
Principle 3: Establish critical limits.
Principle 4: Establish a system to monitor the control status of critical control points.
Principle 5: Determine the corrective actions to be taken when monitoring results indicate a loss of control at a specific CCP.
Principle 6: Establish a certification program to demonstrate that the HACCP system is operating effectively.
Principle 7: Establish files of procedures and records relating to the above principles and their application.
In the food industry, HACCP is being used more and more widely, and it has gradually evolved from a management means and method to a management model or management system. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has worked closely with other international organizations to form a food safety management system based on the HACCP principle, absorbing and integrating the beneficial content of other management system standards.
In order to standardize HACCP system certification, the Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People's Republic of China promulgated the "Implementation Rules for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System Certification" (hereinafter referred to as the Implementation Rules) and the "Basis and Scope of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System Certification (First Batch)" in 2009.
In order to further optimize the food and agricultural product certification system in my country and promote the implementation of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system certification, in accordance with the Food Safety Law of the People's Republic of China, the Certification and Accreditation Regulations of the People's Republic of China and other regulations, the Certification and Accreditation Administration organized the integration of the two certification systems of HACCP system certification for dairy product manufacturers and HACCP system certification for food enterprises into one certification system of HACCP system certification, and integrated the "Implementation Rules for HACCP System Certification for Dairy Product Manufacturers (Trial)" (Announcement No. 16 of the Certification and Accreditation Administration in 2009), the "Implementation Rules for HACCP System Certification for Food Enterprises" into one certification system of HACCP system certification. The "Implementation Rules for HACCP System Certification for Dairy Product Production Enterprises (Trial)" and "Implementation Rules for HACCP System Certification for Food Enterprises" have been integrated and revised. The revised new version of the "Implementation Rules for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System Certification" is now published.
According to the implementation rules, the HACCP system certification certificate is valid for 3 years, and it is required to conduct a supervisory audit on the certified enterprises every year. The first supervisory audit is required to be conducted within 12 months from the last day of the second stage audit. Based on risk analysis, the certification body should plan to implement follow-up investigations on certified organizations by means of unannounced on-site audits, product sampling inspections at production sites, market sampling inspections, questionnaires, etc. The proportion of organizations to be followed up each year should not be less than 5% of the total number of certified organizations. If the number of certified organizations is less than 100, the number of follow-up investigations should not be less than 5.
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP System) Certification Basis:
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System Certification Requirements (V1.0)
Note: When applicable, in order to meet the needs of importing countries (regions), the certification body may use the General Principles of Food Hygiene formulated by the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) as a supplementary certification basis.
HACCP Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points FAQs
1. What are hazards and what are the main hazards in the food production process?
Hazards are defined as potential negative health effects caused by biological, chemical or physical agents or conditions. Examples of hazards in the food production process include metal shavings (physical), pesticides (chemical) and microbial contamination, such as pathogens (biological). The main hazards facing the food industry today are microbial contamination, such as salmonella, eco-oxygen 157: H7, preservatives, germs, bacteria, meat bacteria, etc.
2. What is the importance of HACCP?
In the food production process, the early detection of potential hazards determines the importance of HACCP. By controlling the main food hazards, such as microbial, chemical and physical contamination, the food industry can better provide consumers with consumption safety guarantees, reduce the hazards in the food production process, and thus improve people's health.
3. Is the HACCP standard new? Why has the international community attached so much importance to HACCP in recent years?
HACCP is not a new standard. It was developed in the 1960s by the Pierce Company, NASA and a US military laboratory (Natick area). The original intention of establishing the system was to provide food safety protection for astronauts in space operations. In recent years, with the increasing attention paid to food safety and hygiene by people all over the world, the food industry and its consumers have become the main driving force for companies to apply for HACCP system certification. The significant increase in food poisoning incidents worldwide has stimulated the improvement of economic order and food hygiene awareness. In countries such as the United States, Europe, the United Kingdom, Australia and Canada, more and more regulations and consumers require that the requirements of the HACCP system be turned into market access requirements. Some organizations, such as the National Academy of Sciences of the United States, the National Advisory Committee on Microbiological Food Standards, and the WHO/FAO Nutrition Law Commission, agree that HACCP is the most effective management system to ensure food safety.
4. Compared with traditional food safety control methods, what is unique about HACCP?
Traditional food safety control processes are generally based on "centralized" inspections, final product testing, etc., and use the "look, smell, and cut" method to find potential hazards instead of taking preventive measures. Therefore, there are certain limitations. For example, completing food processing work within the specified time, relying on intuition to predict potential food safety problems, and the high cost of final product inspections, in order to obtain meaningful and representative information, there are great difficulties in collecting and analyzing enough samples. Under the guidance of the HACCP management system principles, food safety is integrated into the design process, rather than the traditional final product testing. Therefore, the HACCP system can provide a system that can play a preventive role and can more economically ensure food safety. HACCP practices in some countries show that the implementation of the HACCP system can more effectively prevent food contamination. For example, statistics from the US Food and Drug Administration show that among aquatic product processing companies, the probability of food contamination in companies that implement the HACCP system is 20% to 60% lower than that of companies that do not implement it.
5. What are the advantages of the HACCP system?
The implementation of the HACCP system has the following advantages:
A. Emphasize the identification and prevention of food contamination risks, overcoming the limitations of traditional approaches to food safety control (through detection, rather than prevention of food safety problems);
B. Have complete scientific basis;
C. By keeping a long-term record of the company's compliance with food safety laws, rather than the degree of compliance on a certain day, government investigators are more efficient and the results are more effective, which helps regulatory authorities conduct investigations; D. Possible and reasonable potential hazards can be identified, even if similar failure problems have not been experienced before. Therefore, it is particularly useful for new operators;
E. Have more flexibility to allow for changes, such as improvements in equipment design, improvements in product-related processing procedures and technology development, etc.
F. Better coordination with the quality management system;
G. It will help improve the competitiveness of food companies in the global market, enhance the credibility of food safety and promote trade development.

[Introduction to Selenium-Rich Product Certification]:
"Selenium-rich products" refer to products where selenium is absorbed and transformed through biological processes, with production and processing procedures meeting certification requirements, ensuring the product's selenium content reaches certified levels.
Selenium-rich products are categorized into two types: naturally selenium-rich, such as soil-derived selenium leading to selenium-rich agricultural products, and supplemented selenium, achieved through selenium-rich fertilizers in soil or selenium-rich feed for livestock to meet meat selenium requirements.
However, any form of selenium supplementation after harvest or during food processing is strictly prohibited.
"Selenium-rich products" emphasize the biological absorption and transformation of selenium, prohibiting any post-harvest or processing supplementation.
According to certification rules, products without certification are not permitted to use the "Selenium-rich product" certification mark on their packaging.
Selenium-rich product certification is an evaluation activity conducted by certifying bodies to assess the compliance of selenium-rich agricultural and food products in production, processing, and operation, based on technical specifications and implementation rules.

Zinc-Fortified Products (Zinc-Fortified Foods) Certification Introduction:
Through biological absorption and transformation of zinc, as well as nutritional fortification methods, zinc content meets specified requirements, creating agricultural products or foods that benefit human health without posing risks.
Enterprises requiring certification for zinc-fortified products (zinc-fortified foods) may contact us for further details on the certification process and specifics.

Introduction to Low GI Food Certification
Low GI foods refer to products containing digestible carbohydrates with a glycemic index (GI) below 55. Using the glycemic index to reasonably arrange diets is highly beneficial for blood sugar control. Therefore, low GI foods are increasingly favored by consumers seeking to manage blood sugar and body weight.
Food GI classification is as follows:
Low GI foods: Glycemic index (GI) ≤55;
Medium GI foods: Glycemic index (GI) 56~69;
High GI foods: Glycemic index (GI) 70~100;
Low GI food certification can guide consumers to select products that help regulate blood sugar and control weight based on their needs when shopping.
Low GI food certification is conducted by third-party organizations.


【Definition of Pure Grain Solid-State Fermented Baijiu】:
Pure grain solid-state fermented Baijiu (distilled spirit with foodstuff - solid fermentation) refers to a white spirit product made from cereal grains (excluding tubers) as raw materials, processed through ingredient mixing, saccharification, fermentation, and distillation under solid-state conditions, without the addition of edible alcohol or non-Baijiu fermentation-derived flavoring substances.
【Requirements for Raw and Auxiliary Materials of Pure Grain Solid-State Fermented Baijiu】:
1. Sorghum must comply with GB/T 8231 and GB2715 standards.
2. Wheat must comply with GB1351 and GB2715 standards.
3. Corn must comply with GB1353 and GB2715 standards.
4. Rice must comply with GB1354 and GB2715 standards.
5. Mung beans must comply with GB/T10460 and GB2715 standards.
6. Brewing water must comply with GB5749 standards.
7. Other raw and auxiliary materials and packaging materials should be sourced from certified production enterprises, with relevant production license copies obtained, verified, and retained.
Production requirements must meet GB/T 23544 "Good Manufacturing Practice for Baijiu Enterprises".
【Application Conditions for Pure Grain Solid-State Fermented Baijiu】:
1. Possession of a production license.
2. Possession of production facilities or authorization to qualified enterprises for production.
3. Enterprises using pure grain solid-state fermentation methods are eligible to apply.
【Benefits of Applying for Pure Grain Solid-State Fermented Baijiu Certification】:
Enterprises obtaining Pure Grain Solid-State Fermented Baijiu certification must strictly adhere to national regulatory requirements during production and sales, subject to supervision by relevant authorities. This not only avoids unnecessary food safety additive issues but also enhances corporate image, promotes high-quality development, elevates brand value, and strengthens consumer confidence and market competitiveness.

Introduction to Supply Chain Security Management System:
The ISO 28000 supply chain security management standard details the requirements for a supply chain security management system and integrates security management with other management; the scope of ISO 28000 covers all activities that an organization controls and influences throughout the supply chain, including transportation.
ISO 28000 was developed in response to the need for common security management standards in the transportation and logistics industry, with the ultimate goal of improving the overall security of the supply chain.
ISO28000, as a supply chain management system specification, provides a framework for organizations that operate or rely on a link in the supply chain for the first time. It can help all sectors of the industry review security risks and implement control and risk mitigation arrangements to manage potential security threats and impacts in the supply chain.
Role and Benefits: It helps all sectors of the industry review security risks and implement control and risk mitigation arrangements to manage potential security threats and impacts in the supply chain.
ISO 28000 applies to:
ISO 28000 is applicable to any size and type of organization at any stage of the supply chain, including procurement, manufacturing, service, warehousing and transportation. It requires organizations to identify and evaluate the elements of their supply chain security management process, including but not limited to: finance, manufacturing, information management, equipment used for packaging and storage, and the transfer of goods between different modes of transportation and locations, and confirm whether adequate security measures have been taken and whether laws, regulations and other requirements are complied with.
ISO 28000 is increasingly becoming a basic requirement for international supply chain companies, and more and more business partners will also make this requirement.
ISO 28000’s role:
As the world economic and trade situation and the international political and economic environment become increasingly complex and uncertain, the supply chains of many Chinese companies are currently facing severe tests. It is very important to carry out supply chain security standardization work to build a safe, controllable and sustainable supply chain.
Today's supply chain spans the globe, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, OEM manufacturers, and outsourcing service providers. Economic globalization means an increasingly unstable business environment, higher user expectations, and shorter product life cycles.
The interdependence of supply chain members in business cooperation also increases the complexity of the supply chain. Coupled with the increasingly uncertain external operating environment, the supply chain becomes more vulnerable to internal and external threats.
At the same time, unpredictable natural disasters, difficult-to-defend against terrorist attacks, and numerous safety accidents in high-risk industries such as transportation, coal mining, and chemicals are constantly threatening the production, warehousing, logistics, sales and other processes in corporate operations.
Coupled with the complexity and interconnectedness of the supply chain network itself and managers' demands for refined management, these internal factors and external threats all highlight the vulnerability of the supply chain.
Therefore, it is particularly important for enterprises to conduct uncertainty analysis on sudden event disturbances, study the transmission mechanism of disaster shocks in the supply chain, improve the security of the supply chain, establish a sound supply chain security management system, and take countermeasures against weak links with high vulnerability to improve the robustness and flexibility of the supply chain.
The standardization of supply chain security management is to summarize the technology and successful practical experience of supply chain security management into common principles and bases for everyone to follow.
Provide guidance on security and resilience for upstream, midstream and downstream enterprises and stakeholders in the supply chain, thereby improving the level of supply chain security management in the whole society and leading the high-quality development of the industry
1. Demonstrate a complete and secure supply chain management system to stakeholders, improving the business capabilities and credibility of the organization;
2. Ensure consistency in the way different upstream and downstream service providers in a supply chain do things;
3. Comprehensively identify and evaluate safety risks to effectively control and reduce safety hazards and impacts in the supply chain.
4. This standard is a management system based on the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle principle, based on the recognized ISO 9001 standard, and can be effectively integrated with ISO 14001 & ISO 45001;
5. After the September 11th incident, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security Customs and Border Protection (CBP) established the Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) to meet the security management requirements of the supply chain. At the same time, organizations in other parts of the world have also issued relevant standards, such as the European Authorized Economic Operators (AEO), the Canadian Partner Protection Measures (PIP) and the World Customs Organization (WCO) to ensure the safety and convenience of global trade and transportation. If an organization wants to meet the requirements of the above standards, implementing ISO 28000 becomes more important and is the most basic requirement.





【Definition of Ecological Farm】:
Based on ecological principles, following the principles of "integrity, coordination, circulation, regeneration and diversity", through overall design and reasonable construction, and adopting a series of sustainable agricultural technologies, the material circulation and energy transformation between organisms and between organisms and the environment are linked, and the agricultural biological-agricultural environmental system is scientifically and rationally combined and managed to obtain the maximum sustainable yield, while achieving a resource-matched, environmentally friendly and food-safe farm.
【Application conditions for ecological farms】
1. Basic conditions:
The applicant must be a family farm, farmer cooperative, enterprise or other entity with independent legal personality, mainly engaged in planting, animal husbandry or aquaculture, and registered for more than 5 years. The applicant is mainly engaged in agricultural production and operation, that is, the income from agricultural production, processing and sales accounts for more than 50% of the total sales income. The farm has clear boundaries, an area of more than 2 hectares, legal land use rights and management rights, no bad credit, serious illegal records, and corresponding supporting documents.
2. Good ecological foundation:
Farmers are highly motivated to participate in the construction of ecological agriculture. The farm is more than 2km away from the pollution source and is located in a non-agricultural product prohibited production area. The functional division is clear, the industrial layout is reasonable, and the circulation chain is smooth. The soil quality of the farm meets the agricultural land soil pollution risk control standards, and there have been no pollution accidents or ecological damage incidents in the past five years. The applicant has its own brand, the quality of agricultural products meets the national food safety standards, and the product packaging materials meet the standards of relevant national regulations. There are complete records of input purchase, use and production management operations, and a quality management system and product traceability system have been initially established.
For other application conditions, please refer to NY/T3667 "Technical Specifications for Ecological Farm Evaluation" issued by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs.
 Organic Chinese herbal medicine certification (including wild Chinese herbal medicine)
Organic Chinese herbal medicine certification (including wild Chinese herbal medicine) GAP (Good Agricultural Practice for the Production of Traditional Chinese Medicines)
GAP (Good Agricultural Practice for the Production of Traditional Chinese Medicines) Certification of authentic herbs
Certification of authentic herbs Certification of products with the same source of food and medicine
Certification of products with the same source of food and medicine Three-Nothing-One-Whole Evaluation (Chinese Herbal Medicine)
Three-Nothing-One-Whole Evaluation (Chinese Herbal Medicine)

Introduction to Organic Chinese Medicinal Materials Certification (including wild Chinese medicinal materials):
Certification of organic products for Chinese medicinal materials includes: Chinese medicinal material cultivation, wild Chinese medicinal materials collection, Chinese medicinal materials processing, Chinese medicinal materials management, etc. The scope of certification is based on the "Organic Product Certification Catalogue", which will be revised and announced by the State Administration for Market Regulation as of December 23, 2022.
The organic catalog products of Chinese herbal medicines that can be applied for at present are: opposite-leaved stemona; creeping stemona; erect stemona; smilax; lily; lily; fine-leaved lily; dark purple Fritillaria (Sichuan Fritillaria); Sichuan Fritillaria; Gansu Fritillaria (Sichuan Fritillaria); smilax Fritillaria (Sichuan Fritillaria); Taibai Fritillaria (Sichuan Fritillaria); Yunnan Polygonatum; Polygonatum sibiricum; Polygonatum sibiricum; Ophiopogon japonicus; Flat Fritillaria; Hubei Ophiopogon japonicus (Mountain Ophiopogon); Asparagus (Asparagus); Smilax glabra (Tusmilax); Small root garlic (Xiebai); Xie (Xiebai); Xinjiang Fritillaria (Ili Fritillaria); Ili Fritillaria (Ili Fritillaria); Polygonatum odoratum; Fritillaria thunbergii; Anemarrhena asphodeloides; Seven-leafed Polygonum multiflorum (Chinese Polygonum multiflorum, Polygonum yunnanensis); Platycladus orientalis; Cibotium barometz (Cynomys chinensis); Herba Lycopodii (Golden Money Grass); Plantago (Plantago, Plantago seed); Plantago asiatica (Plantago, Plantago seed); Dipsacus asper (Dipsacus asper); Scutellaria barbata; Leonurus japonicus (Leonurus virginiana); Salvia miltiorrhiza; Rubus rubescens (Dongling grass); Duwei; Patchouli; Scutellaria baicalensis; Nepeta tenuifolia (Nepeta tenuifolia spike); Huoxuedan (Lianqiancao); Fragrant blue mint (Mountain mint); Prunella vulgaris; Agar grass (Xiancao); Hairy-leaved sweet potato seedling (Ze Lan); Croton; brocade; gansui; euphorbia; qianjinzi; juncus effusus; plum-leaved holly (gangmei); holly; psoralea; sapodilla (large soapberry, soapberry thorn, pig tooth soap); catechu; sharp-leaved senna; narrow-leaved senna; liquorice; kudzu (pueraria root); coin herb; albizzia; multi-order rock astragalus (red astragalus); fenugreek; sophora (sophora flower, sophora horn); mongolica; membranous astragalus; dense flower bean (millettia); dalbergia odorifera (dalbergia); cassia (cassia seed); small cassia (cassia seed); sophora flavescens; timothy; beautiful pea vine (Niu Dali); Qianjinba; flat stem astragalus (Asparagus); Vietnamese Sophora japonica (Sophora japonica); Robinia pseudoacacia (Robinia pseudoacacia); Rhododendron dasyphylla (Manshanhong); Eucommia ulmoides; Broken cloth leaves (cloth residue leaves); Poria cocos (Poria cocos peel); Ganoderma lucidum (Ganoderma lucidum); Ganoderma lucidum (Ganoderma lucidum); Firewood phyllostachys (Phinophora tinctorius); Polyporus umbellatus; Pueraria lobata (Northern Bean Root); Stephania tetrandra; Golden fruit olive; Green cattle gall (Golden fruit olive); Coix lacryma-grass; Light bamboo (Light bamboo leaves, bamboo shavings); Reed (Phragmites australis); Black Trigonosciadium japonicum; Torreya grandis; Yunnan yew; Northeast yew; Green lily; Trichosanthes kirilowii (Trichosanthes kirilowii, Trichosanthes kirilowii peel, Trichosanthes kirilowii, Radix Trichosanthis); Double-sided Trichosanthes kirilowii (Trichosanthes kirilowii Trichosanthes, Trichosanthes peel, Trichosanthes seeds, Radix Trichosanthis); Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Momordica grosvenori; Fritillaria thunbergii; Big puffball; Peeled puffball; Purple puffball; Tribulus terrestris; Houttuynia cordata; Plumeria; Dogbane; Rauwolfia; Vinca rosea; Alpinia officinalis (Big Cardamom); Curcuma zedoaria (Curcuma zedoaria, Pianturmeric, Curcuma); Curcuma guangxiensis (Curcuma zedoaria, Curcuma); Curcuma zedoaria (Curcuma zedoaria, Curcuma); Alpinia officinalis; Alpinia officinalis (Red cardamom); Green shell sand (Amomum villosum); Amomum villosum (Amomum villosum); Alpinia oxyphylla; Coral grass (Swelling knotweed); Viola yedoensis; Abutilon; Green pod leaf (Small tongcao); Himalaya Flower of flag (small tongcao); Chinese flower of flag (small tongcao); yellow grass (pulling root vegetable); Rhodiola rosea; Lobelia; Codonopsis pilosula; Codonopsis pilosula; Codonopsis pilosula; Platycodon grandiflorum; Adenophora volvacea; Adenophora pilosula; Artemisia argyi; Atractylodes macrocephala; Xanthium sibiricum; Atractylodes macrocephala; Atractylodes macrocephala; Pyrethrum cineraria; Sichuan costus root; Gray-haired Sichuan costus root; Thistle; Goose does not eat grass; Tarragon (pepper wormwood); Artemisia absinthium (golden gentian grass); Chrysanthemum; Coltsfoot (coltsfoot flower); Artemisia willow leaf (artemisia willow); Qizhou loach; Costus root; Garlic leaf Brahmannia glutinosa; Senecio lanceolata; Milk thistle; Inula; Hairy stem Siegesbeckia; Siegesbeckia glandularis; Prickly lettuce ( Thistle); wild chrysanthemum; goldenrod; Artemisia spathulata; Artemisia spathulata; Aster; Selaginella pedunculata; Selaginella pedunculata; Andrographis paniculata; Quercus; Brucea brucea; Bletilla striata; Anoectochilus variegatus; Dendrobium tooth-petalum; Dendrobium nobile; Dendrobium huoshanense; Gastrodia elata; Dendrobium candidum; Kochia scoparia; Melia toosendan; Melia azedarach; Polygonum aviculare; Rheum tanguticum; Rheum palmatum; Polygonum multiflorum; Polygonum cuspidatum; Fagopyrum saccharum; Polygonum aviculare; Polygonum rubrum; Polygonum tinctorius; Polygonum rubrum; Cistanche tubulosa; Cistanche deserticola; Dryopteris crassifolia; Evening primrose; Gentiana; Gentiana serrata; Gentiana striata (Gentiana striata) ); Gentiana triflora (gentian); Gentiana scabra (gentian); Gentiana scabra (gentian); Gentiana scabra (twisted); Gentiana scabra (thick stem); Gentiana scabra (small); Deer Hoof Grass (deer mouth grass); Common Deer Hoof Grass (deer mouth grass); Willow Leaf White Front; Gentiana scabra (leaf white front); Niu Pi Xiao; Xu Changqing; White Wei; Creeping White Wei; Grass Ephedra; Ephedra Equisetum; Middle Ephedra; Vitex; Verbena; Single Leaf Vitex; Vitex; Portulaca; Northern Aristolochia (Tianxianteng); Aristolochia (Tianxianteng); Northern Asarum; Seoul Asarum; Hua Asarum; Buddleja; Sea Artemisia (seaweed); Cicadae Corydalis (cicadae); Cicada Flower; Cicada Grass; Aconitum (Aconiti kusnezoffii); Akebia (Chuanketong); Hydrangea vine (Chuanketong); Aconitum (Chuanke, Fuzi); Coptis chinensis; Nasturtium; Altai anemone (Nine-section calamus); Big three-leafed Cimicifuga; Cimicifuga; Xing'an Cimicifuga; Northeast Clematis (Clematis); Cotton Clematis (Clematis); Clematis; Pulsatilla; Inner South Schisandra (Dianxialian); Concave-leafed Magnolia officinalis; Magnolia officinalis; Schisandra chinensis; Schisandra chinensis; Magnolia; Magnolia; Big Blood Caulis; Akebia (Predicted); White Akebia (Predicted); Three-leafed Akebia (Predicted); Forsythia; Ligustrum lucidum; Fraxinus chinensis (Qinpi); Sharp-leaved Fraxinus chinensis (Qinpi); Fraxinus chinensis (Qinpi); Fraxinus chinensis (Qinpi); Equisetum arvense; White smilax; three-leaf cliff creeper (three-leaf green); black smilax; galls on red bran poplar leaves (gallot); galls on green bran poplar leaves (gallot); galls on Rhus chinensis leaves (gallot); Morinda officinalis; Uncaria rhynchophylla; Cnidium officinale; Rubia cordifolia; white flower snake tongue grass; single-petal silk flower (roxburghii); silk flower (roxburghii); mountain thorn rose; goose down cinquefoil (fern); East China raspberry; Pyracantha; golden rosa; Photinia; Peach (peach kernel); Agrimonia (Agrimony); European plum (Prunus mume kernel); Prunus mume; long-handled almond (Prunus mume kernel); white gentian; wolfberry (Lycium bark); Ningxia wolfberry (Lycium bark, Lycium bark); Belladonna; Black wolfberry; Solanum nigrum; Scopolamine (henbane); white flower mandshurica (Datura datura); elderberry; honeysuckle (honeysuckle); Yellow-brown hair honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica); gray felt hair honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica); red gland honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica); South China honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica); Dahurian dwarf ... Hairy Terminalia chebula; Terminalia chebula (Western Qingguo); Pili (hairy Terminalia chebula); Quisqualis; Ziziphus jujuba; Hovenia dulcis; Hovenia dulcis; Phellodendron chinense; Dioscorea chinensis; Phellodendron chinense; Pteris chinensis; Pyrrosia ovata; Pyrrosia ovata; Cynomorium songaricum; Diptera ternata; Acorus calamus; Arisaema mandshurica; Arisaema heterophylla Arisaema; Sterculia lychnophora; Acanthopanax senticosus; Ginseng; Panax notoginseng; Tongtuomu (tongcao); Acanthopanax slender (acanthopanax bark); American ginseng; Rhizoma Cynanchum; Achyranthes bidentata; Atractylodes lancea; Oriental cattail (Puhuang); Water candle cattail (Puhuang); Broad-leaved ten-leaved ten-leaved; Wushan epimedium; Epimedium; Rehmannia root; Picrorhizon; Scrophularia ningpoensis; Scrophularia ningpoensis; Cuscuta chinensis; Thunbergia tengni; Glossy-leaved thunbergia rattan; nettle; ginkgo (gingko); mao leucorrhiza; corydalis (yuanhusuo); iris (chuan iris); iris; crocus (saffron); melon seeds; polygala; tangerine and its cultivars (tangerine peel, tangerine seed, tangerine peel, green peel); phellodendron (guan phellodendron); Huazhou pomelo (hua juhong); yellow peel tree (phellodendron); osmanthus; thyme (osmanthus); two-sided needle; three-forked bitter orange; sour orange, bitter orange, stinky orange and their cultivars (citrus aurantium, citrus aurantium); white fresh; evodia rutaecarpa; stone tiger (evodia rutaecarpa); sparse hair evodia rutaecarpa; oriental water plantain; mountain pepper (piper, mountain litsea); camphor (natural borneol); lindera; inner mongolia lithospermum; Xinjiang lithospermum; dwarf tea (dwarf tea); cinnabar root; wood butterfly; cordyceps sinensis; tiger eye dieffenbachia; roselle; deer antler Grass; valerian; longevity; cardamom; white cardamom (cardamom); garlic orchid (mountain cilia); geranium; galangal; tabulaeformis (pine pollen, pine joint); bamboo ginseng; sandalwood; perilla; ground ding grass (bitter ground ding); nard; ivy (green wind vine); citron (citron); ailanthus (toona bark); tamarisk (west river willow); ground shoot (ground ginseng); Chinese sage (stone sees the thread); creek yellow grass; leaf beads; sappan wood; colored velvet leather cover (veris versicolor); yellow rattan; hairy ivy (green wind vine); mountain fragrant round (mountain fragrant round leaf); wind vine (sea breeze vine); changshan; trachelospermum (trachelospermum vine); Java white cardamom (cardamom); creeping pot grass; striped leaf inula (gold boiling grass); chrysanthemum intestine (polygonum aviculare); Eurasian inula (inula); inula (inula, golden =Fuel grass); hanging stone lycopodium (stone hanging plant); azalea orchid (mountain ci mushroom); Yunnan single garlic orchid (mountain ci mushroom); wart-haired swertia (when medicine); green leaf gall; Tongguan vine; Perilla (persimmon bark); large-leaved callicarpa; Guangdong callicarpa; scutellaria baicalensis (geranium); wild geranium (geranium); multi-flowered anemone (two-pointed); small buttercup (cat's claw grass); yellow flower clematis (clematis through bone grass); ground maple bark; horse chestnut (Sala seed); Tianshi chestnut (Sala seed); Zhejiang horse chestnut (Sala seed); red euphorbia; tooth-leaved flat-core wood (Ruren); Ruren (Ruren); Potentilla; three white grass; wild carrot (Southern Crane lice); yellow flower grass; iris; powder-backed yam (Powder-backed yam); Hypericum perforatum (Hypericum perforatum); pseudo-porcupine quill (three needles ); spoon-leaved berberis (three needles); fine-leaved berberis (three needles); small coptis thorn (three needles); peach seven (small leaf lotus); Yinxing grass (North Liu Jinu); short-tube rabbit ear grass (Honglian); Hubei Fritillaria; Ricinus (castor beans); thin bamboo (Tianzhuhuang); green-skinned bamboo (Tianzhuhuang); big-headed bamboo (bamboo shavings); green-stalked bamboo (bamboo shavings); Momordica (Momordica seeds); Hibiscus (Hibiscus leaves); Indigo (Polygonum indigo leaves); Soft-fleshed kiwifruit (vine pear root); southern sour jujube (wide jujube); Masson pine (pine pollen, pine knot); whole leaf chicory (North Patrinia); Guangzhou acacia (chicken bone grass); Artemisia annua (artemisia annua); Indigofera (South Isatis root); Tiankui (Tiankui seeds); Dianthus (Dianthus); Trumpet creeper (Poplar creeper); wild papaya.
List of application materials: Same as for organic planting and wild collection certification projects.

【Brief description of GAP (Good Manufacturing Practice for Chinese Herbal Medicines)】:
Announcement of the National Medical Products Administration, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, the National Forestry and Grassland Administration, and the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine on the promulgation of the "Quality Management Standards for the Production of Traditional Chinese Medicines" (No. 22 of 2022);
In order to implement the "Implementation Plan for Major Projects for the Revitalization and Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine" issued by the General Office of the State Council, orderly promote the implementation of the "Good Manufacturing Practice for Chinese Medicinal Materials" (GAP for Chinese Medicinal Materials), promote standardized production of Chinese medicinal materials, improve the quality of Chinese medicine from the source, and promote the inheritance, innovation and high-quality development of Chinese medicine, in accordance with the working ideas of "being politically conscious, strengthening supervision, ensuring safety, promoting development, and benefiting people's livelihood" and the work deployment of the State Food and Drug Administration's "Several Measures on Further Strengthening Scientific Supervision of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Promoting the Inheritance and Innovation of Traditional Chinese Medicine", the State Food and Drug Administration has decided to carry out the demonstration construction of GAP supervision implementation for Chinese medicinal materials. The drug regulatory departments of Anhui, Guangdong, Sichuan and Gansu provinces will serve as the task-bearing units to promote the demonstration construction, and other provincial drug regulatory departments can take the initiative to carry out it according to work needs.
[Excerpt from "Quality Management Standards for Chinese Medicinal Materials Production"]:
[Article 6]: Enterprises shall establish an effective supervision and management mechanism for the main production units of the base to achieve on-site guidance, supervision and record-keeping of key links; unify the planning of production bases, unify the supply of seeds, seedlings or other breeding materials, unify the management measures for inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides or feed, veterinary drugs, unify the planting or breeding technical regulations, unify the harvesting and processing technical regulations at the place of origin, and unify the packaging and storage technical regulations.
[Article 9]: Enterprises shall establish a quality traceability system for Chinese medicinal materials production to ensure that key links in the entire process, from production sites, seeds and seedlings or other propagation materials, planting and breeding, harvesting and processing at the place of origin, packaging, storage and transportation to shipment, can be traced; enterprises are encouraged to use modern information technology to build a traceability system.
【Article 11】: Enterprises shall formulate quality standards for Chinese medicinal materials, and the standards shall not be lower than the current statutory standards.
(1) Determine the quality control indicators based on the actual production situation, which may include: medicinal material properties, inspection items, physical and chemical identification, extracts, fingerprints or characteristic spectra, indicators or the content of active ingredients; control standards for pesticide residues or veterinary drug residues, heavy metals and harmful elements, mycotoxins and other toxic and harmful substances in medicinal materials;
【Article 12】: Enterprises shall formulate standards for seeds, seedlings or other propagation materials of Chinese medicinal materials.
【Article 35】: Enterprises shall clearly identify the origin and germplasm of seeds, seedlings or other propagation materials used, including species, subspecies, variants or forms, farm varieties or selected varieties; the origin of the species used for planting or breeding shall comply with relevant standards and regulations. The use of medicinal wild plant resources listed in the "National Key Protected Wild Plant List" shall comply with relevant laws and regulations.
[Article 15]: The person in charge of the enterprise is responsible for the quality of Chinese medicinal materials; the enterprise should be equipped with a sufficient number of production and quality management personnel with qualifications corresponding to their job responsibilities; the person in charge of production and quality management should have a college degree or above in Chinese medicine, pharmacy or agronomy and other related majors and have more than three years of practical experience in Chinese medicinal materials production and quality management, or have more than five years of practical experience in Chinese medicinal materials production and quality management, and all must undergo training in this specification.
[Article 27]: Chinese medicinal materials production bases should generally be located in authentic production areas. If they are located in non-authentic production areas, sufficient literature or scientific data should be provided to prove their suitability.

Brief description of authentic Chinese herbal medicine certification:
【Authentic production area】:
The Chinese medicinal materials produced in this production area have been selected through long-term clinical application of traditional Chinese medicine. Compared with the same Chinese medicinal materials produced in other regions, they have better quality and efficacy, stable quality and high popularity.
【Authentic medicinal materials】;
The so-called authentic medicinal materials, also known as genuine medicinal materials, is a special term for high-quality and pure medicinal materials. It refers to medicinal materials with a long history, suitable origin, excellent varieties, abundant output, exquisite preparation, outstanding efficacy and regional characteristics.
[Differences and similarities between authentic medicinal materials and geographical indications]: (Excerpt from part of the information released by the Trademark Office of the State Intellectual Property Office on 2021-12-0307:58).
1. [Similarities between authentic medicinal materials and geographical indications]
(1) [Both are also limited by origin]
my country's Trademark Law also stipulates that geographical indications must indicate that a product originates from a certain region.
Similarly, authentic medicinal materials also have distinct characteristics of origin. One of the characteristics of authentic medicinal materials is that they come from a specific natural environment. The original meaning of "authentic" medicinal materials refers to medicinal materials that are local specialties. After a long period of development of traditional Chinese medicine, they have become representatives of medicinal materials with high quality and good efficacy.
(2) [Both have a quality, reputation or other definite characteristics which are due to their place of origin]
Geographical indications require that the quality, reputation or other characteristics of the products using geographical indications must essentially depend on the natural or human factors of the place of origin. The Trademark Law of the United States stipulates that the specific quality, reputation or other characteristics of the goods using geographical indications are mainly determined by the natural or human factors of the region.
Similarly, the specific quality and reputation of authentic medicinal materials come from the natural and human factors unique to their authentic production areas. Natural factors are a prerequisite for the formation of authentic medicinal materials. The natural factors that affect the growth and development of authentic medicinal materials include sources, climate, soil, sunlight, water, etc. Soil conditions affect the growth and accumulation of medicinal materials, mineral elements in the soil affect the nutrient absorption of plants, the content and ratio of air and water in the soil affect the respiration of plants, and sunlight and climate conditions determine the variety, quantity and reproduction of microorganisms around plants. After long-term observation and comparison, ancient medical scientists found that even widely distributed medicinal materials have different qualities due to different natural conditions, and gradually formed the concept of "authentic medicinal materials". For example, the traditional harvesting season of peony bark is the second and eighth months of the lunar calendar, that is, early spring and late autumn. The accumulation of ingredients such as paeoniflorin and paeonol contained in it has two peak periods in a year, namely May-June and September-October. Since spring is the time for stem and leaf growth and root nutrients to rise, the root bark dug at this time is of poor quality. In addition, spring is rainy and the medicinal materials are not easy to dry. Therefore, the harvesting of peony bark is mostly chosen in autumn. The medicinal materials harvested at this time are powdery, full in shape, and of high quality and yield. Specific medicinal material planting, harvesting and processing techniques are important guarantees for the excellent efficacy of authentic medicinal materials.
(3) [The two have basically the same form of expression]
Geographical indications are usually composed of "geographical name + common name". Geographical name refers to the formal and long-established or commonly accepted name that refers to a specific geographical entity or geographical area. Common name refers to the name of a certain type of product that is commonly used within a certain range2.
The names of most authentic medicinal materials are the same as "authentic production area + medicinal material name". For example, Dong'e Ejiao, Huaishan Yam, Chuanbeimu, etc.
2. [Differences between authentic medicinal materials and geographical indications]
(1) [The range of products with geographical indications is wider than that of authentic medicinal materials]
The types of goods currently registered as collective trademarks and certification trademarks of geographical indications include vegetables, fruits, poultry, grains, handicrafts, medicinal materials, etc. The scope of objects of authentic medicinal materials is relatively narrow, limited to animals, plants or mineral products with medicinal value.
(2) [Product quality requirements for authentic medicinal materials are stricter than those for geographical indications]
The "collective trademark and certification trademark" protection system of the State Intellectual Property Office requires that a product be marked as coming from a certain region, and that the specific quality, reputation or other characteristics of the product are mainly determined by the natural or cultural factors of the region. It does not stipulate that the quality of geographical indications is higher than that of ordinary products.
Authentic medicinal materials are different from this. The reason why authentic medicinal materials are "authentic" is that they are "higher quality and better efficacy" than ordinary medicinal materials. In terms of quality, authentic medicinal materials have higher content of active ingredients, less pesticide residues and heavy metal ions than ordinary Chinese medicinal materials.

List of Chinese medicinal materials with both medicinal and edible properties
The health administration department of the State Council has released four lists of substances that are both food and Chinese medicinal materials. There are 106 substances in total. They are:
[First Batch] Notice of the Ministry of Health on Further Standardizing the Management of Health Food Ingredients (Weifajianfa [2002] No. 51):
Clove, star anise, amaranth, sword bean, fennel, thistle, yam, hawthorn, purslane, black snake, black plum, papaya, hemp seed, daidai flower, polygonatum, licorice, angelica, ginkgo, white lentil, white lentil flower, longan meat (longan), cassia seed, lily, nutmeg, cinnamon, emblica, bergamot, almond (sweet and bitter), sea buckthorn, oyster, gorgon fruit, pepper, red bean, donkey-hide gelatin, chicken gizzard, malt, kelp, jujube (jujube, sour jujube, black jujube), monk fruit, Prunus mume, honeysuckle, green fruit, houttuynia, ginger (ginger, dried ginger), Citrus aurantium, wolfberry, gardenia, Amomum villosum, Sterculia lychnophora, Poria, citron, Elsholtzia, peach kernel mulberry Leaves, mulberry, tangerine peel, platycodon, alpinia oxyphylla, lotus leaf, radish seed, lotus seed, galangal, light bamboo leaf, light black bean, chrysanthemum, chrysanthemum perilla, perilla seed, kudzu root, black sesame, yellow mustard, polygonatum, hemp, black pepper, sophora japonica, sophora japonica, dandelion, honey, torreya grandis mulberry leaf, mulberry, tangerine peel, platycodon, alpinia oxyphylla, lotus leaf, radish seed, lotus seed, galangal, light bamboo leaf, light black bean, chrysanthemum, chicory, yellow mustard, polygonatum, perilla, perilla seed, kudzu root, black sesame, black pepper, sophora japonica, sophora japonica, dandelion, honey, torreya grandis, spiny jujube kernel, fresh white imperata root, fresh reed root, pit viper, tangerine peel mint, coix seed, scallion, raspberry, patchouli.
[Second batch] Announcement on 6 new substances that are traditionally both food and Chinese medicinal materials, including Angelica sinensis (No. 8, 2019):
Angelica, Kaempferia galanga, saffron (also known as "saffron" in spices and condiments), cardamom, turmeric, and piper longum.
[Third Batch] Announcement on 9 new substances that are traditionally both food and Chinese medicinal materials, including Codonopsis pilosula (No. 9, 2023):
Codonopsis pilosula, Cistanche deserticola (desert), Dendrobium officinale, American ginseng, Astragalus, Ganoderma lucidum, Cornus officinalis, Gastrodia elata, Eucommia ulmoides leaves.
[Fourth batch]. Announcement on 4 substances, including Rehmannia glutinosa, which are traditionally both food and Chinese medicinal materials in 2024:
Rehmannia root, Ophiopogon japonicus, Asparagus cochinchinensis, and Citrus aurantium.
Definition of high-quality food and medicine products
Products produced in accordance with the T/HNYJNYXH "Standards for High-quality Food and Medicine Products" and in line with the product varieties specified in the national "Catalogue of Food and Medicine Products", can be eaten by people and used as medicine, and have specific functions.
Products that meet the requirements of the "Catalogue of Food and Drug Products" can apply for high-quality food and drug products certification. They can only obtain the certificate after passing the review of a third-party certification agency.

【Three-No and One-Complete Chinese Medicinal Materials Evaluation】Introduction:
Background: The quality and authenticity of Chinese herbal medicines, the primary processing and production of Chinese herbal medicines are important sources and key links to support the development of the entire Chinese medicine industry. In recent years, my country's Chinese herbal medicine industry has been developing and standardizing, but affected by various factors, there are still some problems in the Chinese herbal medicine industry, such as the decline in the quality of Chinese herbal medicines, the excessive residues of sulfur dioxide, heavy metals and pesticides, etc., which have been repeatedly banned, thus affecting the sustainable development of Chinese medicine.
In this context, promoting the standardized construction of Chinese medicinal materials bases, standardizing the production process of Chinese medicinal materials, and improving production management procedures are the only way for the development of the Chinese medicine industry. This document aims to establish a guide for the construction of "three-no and one-full" medicinal materials bases, which is of great significance for guiding and standardizing the construction of Chinese medicinal materials bases.
The "Three No and One Complete" Chinese Medicinal Materials Standard and the "Guidelines for the Construction of "Three No and One Complete" Medicinal Materials Bases" were issued by the China Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine and will be implemented on January 15, 2024.
[Concept and definition of "three no and one complete" medicinal materials]:
The Chinese medicinal materials are grown and stored without sulfur, without excessive aflatoxin, without pollution (including no excessive pesticide residues, no excessive heavy metals, no use of growth regulators to promote the growth of harvested organs), and with the entire process traceable.
[Basic requirements for declaring three-no and one-complete medicinal materials]:
1. The planting base should be located in the authentic production area or main production area, avoiding grain production areas and public welfare forests.
2. The planting area of a single variety should not be less than 1,000 mu, and the planting area of rare and endangered varieties and facility-cultivated varieties should be more than 200 mu.
3. Relevant technical regulations and operating procedures for “three no’s and one complete” should be established.
4. The management of production bases, seeds, seedlings, seed sources, and planting should comply with the provisions of the "Quality Management Standards for Chinese Medicinal Materials Production" of the State Food and Drug Administration.
5. Processing at the origin should comply with the relevant requirements of SB/T 11183 "Technical Specifications for Processing of Chinese Medicinal Materials at the Origin" issued by the Ministry of Commerce of the People's Republic of China.
6. Packaging should comply with the relevant requirements of SB/T 11182 "Technical Specifications for Packaging of Traditional Chinese Medicines" issued by the Ministry of Commerce of China.
7. The quality standards shall include but are not limited to the indicators specified in the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China: limit indicators such as sulfur dioxide, pesticide residues, heavy metals, and aflatoxins. The standards shall not be lower than the relevant requirements of the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China.
[Key technical control points of three-no and one-full medicinal materials]:
1. No fumigation
Sulfur fumigation should not be used in the processing stage at the place of origin, sulfur fumigation should not be used in the warehousing stage, and aluminum phosphide fumigation should not be used in the warehousing stage.
2. No aflatoxin exceeding the standard
2.1 Prevent aflatoxin during the planting process: Reasonable density planting, not too high planting density, strengthen field management, and avoid aflatoxin contamination in medicinal materials.
2.2 Prevent aflatoxin during processing: Process and dry in time. Chinese medicinal materials that are not completely dried should not be piled up and stored for a long time. The utensils and facilities involved in the processing process at the place of production should avoid aflatoxin contamination.
2.3 Prevent aflatoxin during storage: The storage facility configuration and stacking management should comply with the requirements of SB/T 11094 "Specifications for Storage Management of Traditional Chinese Medicines". Stacking should not be too high, and modern storage and preservation technologies and equipment such as controlled atmosphere can be used.
2.4 Prevent aflatoxin during transportation: Transportation vehicles should avoid aflatoxin contamination, and transportation should be avoided on rainy days. Transportation in humid seasons should be moisture-proof.
3. Key points of pollution-free technology
According to the type of each Chinese medicinal material, pollution-free and reasonable fertilization and pollution-free integrated pest and disease control procedures should be formulated, and the dosage, frequency, time, safe interval, protective measures, etc. of the pesticide types should be specified. The application amount and safe interval should be controlled in accordance with the requirements of the "Guidelines for the Rational Use of Pesticides" GB/T8321.1-5.
Highly toxic, highly toxic, and high-residue pesticides prohibited by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, as well as other pesticides restricted for use on Chinese medicinal materials, should not be used. Growth regulators (such as growth enhancers) should not be used.
4. Traceability of the entire process of Chinese herbal medicine
The whole process traceability of Chinese medicinal materials should include the whole process of seed and seedling production, planting, field management, pest and disease control, harvesting, processing at the origin, packaging, warehousing logistics, quality, etc. Specific information includes origin, origin, source, plot information, operation parameters, operation date, operator, facilities and equipment used, items used, meteorological data and other information. It can record each operation link, different growth and development stages, and use investment products and other image data.
The Chinese medicinal materials traceability system can be used to achieve traceability by scanning codes, and the Internet of Things technology can be used to access climate monitoring and surveillance equipment.
[Which companies can apply for the “three no and one complete” medicinal material evaluation]?
Any medicinal material raw material enterprise of a certain scale can apply. The scope of application includes: medicinal raw materials derived from medicinal plants, medicinal animals and other resources, which are used in the production of Chinese herbal medicines and Chinese medicine preparations after standardized planting (including ecological planting, wild cultivation and simulated wild cultivation), harvesting and processing at the place of production.

Geographical Indication Trademark (National Intellectual Property Administration)
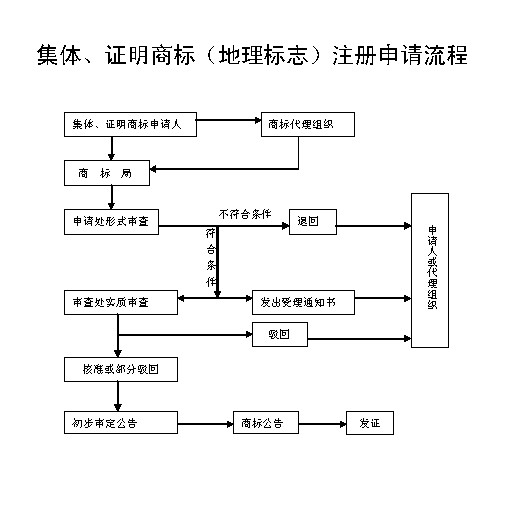

Brief description of authentic Chinese herbal medicine certification:
【Authentic production area】:
The Chinese medicinal materials produced in this production area have been selected through long-term clinical application of traditional Chinese medicine. Compared with the same Chinese medicinal materials produced in other regions, they have better quality and efficacy, stable quality and high popularity.
【Authentic medicinal materials】;
The so-called authentic medicinal materials, also known as genuine medicinal materials, is a special term for high-quality and pure medicinal materials. It refers to medicinal materials with a long history, suitable origin, excellent varieties, abundant output, exquisite preparation, outstanding efficacy and regional characteristics.
[Differences and similarities between authentic medicinal materials and geographical indications]: (Excerpt from part of the information released by the Trademark Office of the State Intellectual Property Office on 2021-12-0307:58).
1. [Similarities between authentic medicinal materials and geographical indications]
(1) [Both are also limited by origin]
my country's Trademark Law also stipulates that geographical indications must indicate that a product originates from a certain region.
Similarly, authentic medicinal materials also have distinct characteristics of origin. One of the characteristics of authentic medicinal materials is that they come from a specific natural environment. The original meaning of "authentic" medicinal materials refers to medicinal materials that are local specialties. After a long period of development of traditional Chinese medicine, they have become representatives of medicinal materials with high quality and good efficacy.
(2) [Both have a quality, reputation or other definite characteristics which are due to their place of origin]
Geographical indications require that the quality, reputation or other characteristics of the products using geographical indications must essentially depend on the natural or human factors of the place of origin. The Trademark Law of the United States stipulates that the specific quality, reputation or other characteristics of the goods using geographical indications are mainly determined by the natural or human factors of the region.
Similarly, the specific quality and reputation of authentic medicinal materials come from the natural and human factors unique to their authentic production areas. Natural factors are a prerequisite for the formation of authentic medicinal materials. The natural factors that affect the growth and development of authentic medicinal materials include sources, climate, soil, sunlight, water, etc. Soil conditions affect the growth and accumulation of medicinal materials, mineral elements in the soil affect the nutrient absorption of plants, the content and ratio of air and water in the soil affect the respiration of plants, and sunlight and climate conditions determine the variety, quantity and reproduction of microorganisms around plants. After long-term observation and comparison, ancient medical scientists found that even widely distributed medicinal materials have different qualities due to different natural conditions, and gradually formed the concept of "authentic medicinal materials". For example, the traditional harvesting season of peony bark is the second and eighth months of the lunar calendar, that is, early spring and late autumn. The accumulation of ingredients such as paeoniflorin and paeonol contained in it has two peak periods in a year, namely May-June and September-October. Since spring is the time for stem and leaf growth and root nutrients to rise, the root bark dug at this time is of poor quality. In addition, spring is rainy and the medicinal materials are not easy to dry. Therefore, the harvesting of peony bark is mostly chosen in autumn. The medicinal materials harvested at this time are powdery, full in shape, and of high quality and yield. Specific medicinal material planting, harvesting and processing techniques are important guarantees for the excellent efficacy of authentic medicinal materials.
(3) [The two have basically the same form of expression]
Geographical indications are usually composed of "geographical name + common name". Geographical name refers to the formal and long-established or commonly accepted name that refers to a specific geographical entity or geographical area. Common name refers to the name of a certain type of product that is commonly used within a certain range2.
The names of most authentic medicinal materials are the same as "authentic production area + medicinal material name". For example, Dong'e Ejiao, Huaishan Yam, Chuanbeimu, etc.
2. [Differences between authentic medicinal materials and geographical indications]
(1) [The range of products with geographical indications is wider than that of authentic medicinal materials]
The types of goods currently registered as collective trademarks and certification trademarks of geographical indications include vegetables, fruits, poultry, grains, handicrafts, medicinal materials, etc. The scope of objects of authentic medicinal materials is relatively narrow, limited to animals, plants or mineral products with medicinal value.
(2) [Product quality requirements for authentic medicinal materials are stricter than those for geographical indications]
The "collective trademark and certification trademark" protection system of the State Intellectual Property Office requires that a product be marked as coming from a certain region, and that the specific quality, reputation or other characteristics of the product are mainly determined by the natural or cultural factors of the region. It does not stipulate that the quality of geographical indications is higher than that of ordinary products.
Authentic medicinal materials are different from this. The reason why authentic medicinal materials are "authentic" is that they are "higher quality and better efficacy" than ordinary medicinal materials. In terms of quality, authentic medicinal materials have higher content of active ingredients, less pesticide residues and heavy metal ions than ordinary Chinese medicinal materials.

Bio-based Products (PEOP)
Refers to products derived from biological sources (including plants, animals, microorganisms, agriculture, forestry, fisheries, animal husbandry, sideline products, pharmaceuticals, and other biological materials) that undergo processing to possess properties such as renewability, biodegradability, environmental friendliness, and sustainability. These include bio-based raw material products, bio-based certified products, bio-resource recycled products, products with recognized ecological labels, and innovative bio-based products with independent intellectual property rights.
Bio-based Products (PEOP) Application Scope:
(1) Bio-based raw material products;
(2) Bio-based certified products;
(3) Bio-resource recycled products;
(4) Products with recognized ecological labels, trademarks, or certifications;
(5) Innovative bio-based products with independent intellectual property rights.

Brief Introduction to Green Food Standard System
The green food standard system is the technical carrier of the green food development concept, the technical guide for green food production and management, and the technical guarantee for the high-quality development of the green food industry. Based on the positioning of high-quality products and aiming at the international advanced level, the China Green Food Development Center follows the principle of "giving equal importance to safety and quality, combining advancement and practicality", and focuses on implementing the whole-process quality control concept of "from land to table". It has established a set of standard systems with accurate positioning, reasonable structure and distinctive characteristics, including four parts: production environment quality standards, production technology standards, product standards, packaging, storage and transportation standards, which regulate all production links of green food production before, during and after production.
As of 2023, there are 143 effective green food standards (including 14 guideline standards and 129 product standards). The promulgation and implementation of these standards provide a basis and criteria for guiding and regulating the production behavior, quality and technical testing, logo licensing review and post-certification supervision of green food, and play an irreplaceable role in promoting the high-quality development of the green food industry.
Brief Introduction of Green Food Production Materials
The green food production materials certification trademark is registered with the State Trademark Office to identify and certify that the production materials are safe, effective, and environmentally friendly and are suitable for green food production.
The green living materials logo is a certification trademark registered with the State Trademark Office. The China Green Food Association is the registrant of the green living materials trademark, and its exclusive right is protected by the Trademark Law of the People's Republic of China.
The scope of the green raw materials logo use license includes: fertilizers, pesticides, feed and feed additives, veterinary drugs, food additives, and other production inputs related to green food production.
Brief Introduction to the National Standardized Production Base of Green Food Raw Materials
The national standardized production base for green food raw materials (hereinafter referred to as the base) refers to a planting area or breeding site that meets the environmental quality standards of green food production areas, implements production and management in accordance with green food technical standards and full-process quality control system requirements, establishes and improves an effectively operating base management system, has a certain scale, and has been reviewed and approved by the China Green Food Development Center (hereinafter referred to as the Center).
In principle, the construction of the base shall be organized and implemented by the county-level people's government, with the goal of demonstrating the green development of agriculture and consolidating the foundation for the development of green food. Adhere to the principle of "government promotion, industrialized operation, relatively concentrated and contiguous, and moderate scale development", promote the regional layout, standardized production, industrialized operation, large-scale development and branding of agricultural products, enhance agricultural competitiveness, promote agricultural efficiency and increase farmers' income. Implement various standards and systems for the whole process of green food quality control, comprehensively promote standardized production of green food, strengthen the ability to connect production and marketing, provide green food production enterprises with the required high-quality raw materials, and gradually become the main supplier of raw materials for green food processing and breeding enterprises.
Base construction and management work includes creation, acceptance, renewal and supervision. The center is responsible for the review and approval of the base and the supervision of the base supervision work. The provincial green food working agency (hereinafter referred to as the provincial working agency) is responsible for the acceptance and preliminary review of the base creation, acceptance and renewal application within the administrative area, and is responsible for the guidance and supervision of base construction. The base construction unit is responsible for the construction and daily management of the base, accepts the supervision and management of the provincial working agency, ensures the quality and safety of the base products, and is responsible for the quality and reputation of the base raw materials.

【Introduction to Green Supply Chain Management Evaluation and Certification】:
Green supply chain management evaluation and certification integrates "green" and "environmental awareness" into the entire supply chain, analyzes the factors that affect the environment in the supply chain management process from aspects such as product design, raw material production, supply process, production process, sales, transportation and use, recycling and reuse, and proposes the basic ideas, research conditions, framework system and evaluation methods of green supply management. The purpose is to enhance the perceptual understanding of the green supply chain and the importance of supply chain management to environmental protection.
Green supply chain management has the characteristics of fully considering environmental issues, emphasizing data sharing among suppliers, closed-loop operation, embodying the idea of parallel engineering, and applying modern network technology. Green supply chain management is not only a corporate management method that takes into account both environmental and economic benefits, but also an effective policy means for the country to use market mechanisms to achieve energy conservation and emission reduction and economic development in parallel.
[Benefits of green supply chain management system to enterprises]:
1. National standard certification and national recognition can enhance the green image of enterprises. Enterprises that implement green supply chains can establish the message that their products are safe and reliable and that they value social responsibility, and can more easily gain the recognition and trust of dealers and consumers; thus, improving the competitiveness of enterprises in the market;
2. Implement environmental assessment of the green supply process to maximize resource utilization, reduce resource consumption, reduce operating costs, and reduce or eliminate environmental pollution.
3. Enterprises seek alliances to implement green supply chains in the fierce market competition. In the green supply chain, they can integrate with upstream and downstream enterprises, complement each other's advantages, and combine strengths to bring more benefits to the entire supply chain.
5. Green technology trade barriers can be avoided. Many countries in the world, especially developed countries, attach importance to ecological issues and have established corresponding technical clauses and environmental protection laws and regulations. If companies want to survive for a long time, they must make their products meet the corresponding green standards, and to achieve these standards, they must implement a green supply chain.
[Required conditions for green supply chain certification applicants]:
1. The applicant organization should obtain a business license or industry license;
3. The applicant organization should establish a system in accordance with the certification standards and operate it effectively for more than 3 months;
4. The applicant organization has not been subject to administrative penalties by the competent government department in the past year, and has not been included in the list of seriously dishonest entities in national credit information;
5. Other conditions specified in the standards.

Definition of Zero-carbon Farm
Based on the evaluation considering only the impact type of climate change, farm carbon emissions expressed in carbon dioxide equivalent are less than or equal to the greenhouse gas emission reduction and carbon sequestration within the farm during the planting season.
Soil carbon sequestration refers to the increase in carbon pool in farmland soil formed by agricultural operations due to the increase of organic matter through artificial measures.
Process emissions refer to greenhouse gas emissions generated by production processes such as planting and fertilization, waste disposal, and rice field flooding during the production of agricultural products, as well as changes in soil organic carbon reserves.
[Basic requirements for zero-carbon farms]:
1. The farm should have clear boundaries and legal land use rights and/or legal business certification documents.
2. Farm producers or operators should establish and optimize relevant sustainable agricultural management systems, institutions and implementation plans.
3. Farms should implement new technologies or projects for emission reduction and carbon fixation, and actively adopt measures such as soil carbon fixation, crop-livestock cycle, biodiversity, reduction of fertilizers and pesticides, and water and energy conservation.
4. Agricultural production data should be kept intact, documented and recorded, and the use of digital technology for collection and monitoring is encouraged to meet the needs of calculating farm carbon emissions and carbon sequestration and emission reductions.
【Greenhouse gas emission range】:
When conducting a farm carbon emissions assessment, the amount of greenhouse gases emitted into and removed from the atmosphere should be recorded. Assessments of greenhouse gas emissions and removals come from a variety of processes, including but not limited to:
a) Energy use; b) Combustion process; c) Planting process; d) Fertilizer application process; e) Waste disposal process.
【Zero Carbon Farm Evaluation】
Farm carbon emissions and carbon sequestration reduction should have the same boundaries and time periods. When the farm's greenhouse gas emissions are less than or equal to the carbon sequestration reduction generated by the farm's implementation of carbon sequestration reduction projects, it can be identified as a zero-carbon farm and an evaluation report will be issued.
Crops that meet the technical specifications for zero-carbon agricultural product evaluation can apply for zero-carbon agricultural product certification.
SERVICE PROCESS
We customize one-to-one coaching solutions and one-stop services based on the specific circumstances of the enterprise
Signing of service contract
Signing of service contract
Consulting Training Standards
Consulting Training Standards
Perfect project planning
Perfect project planning
Establishing a certification system
Establishing a certification system
Internal audit run
Internal audit run
On-site audit (jury)
On-site audit (jury)
Material filing and rectification
Material filing and rectification
Obtain certification
Obtain certification
- Add time:2025-10-24Focus on resources, economy, and ecology to jointly craft the high-quality '14th Five-Year Plan' blueprintNatural resources are the material foundation for the development of human society. Harmony between humanity and nature is an essential requirement for achieving Chinese-style modernization. During the '14th Five-Year Plan' period, China's natural resource base has become more robust. By the end of 2024, the country's arable land area reached 1.94 billion acres, firmly safeguarding the red line of farmland protection. China is the fastest-growing and largest contributor to global greening efforts. The national forest coverage rate reached 25.09%, an increase of about 2 percentage points from 2020. Forest stock volume reached 20.988 billion cubic meters, achieving the 2030 target for climate change mitigation contributions ahead of schedule.
- Add time:2025-06-24Nanjing State Environmental Protection issued the first electronic certificate of EU 2018/848, the most stringent new organic regulation in the European Union.On June 17, 2025, Nanjing SINOTRANS successfully issued its first EU organic certification certificate with electronic signature on the EU Trade Control and Expert System (TRACES system for short) and EU organic regulation EU 2018/848, which marks that Nanjing SINOTRANS is fully capable of meeting the requirements of the new EU organic regulation framework. SINOTRANS has fully equipped with the certification service capacity and level in line with the requirements of the new EU organic regulatory framework.
- Add time:2025-06-07NCA Secretariat on further standardization of "no resistance" certification activities of the circularRecently, some certification bodies to carry out their own "non-antibiotic" certification activities revealed that the certification basis is not standardized, the certification rules are not scientific, and the certification activities are not serious. Some of the certified organizations have excessive use of "non-antibiotic" certification, misleading consumers and other issues. At present, there is no clear consensus on the concept of "non-antibiotic" and the certification basis of various organizations is not uniform, in order to strictly implement the "four strictest" requirements for food safety and standardize the certification activities of "non-antibiotic", we hereby notify the following matters. In order to strictly implement the "four strictest" requirements for food safety and standardize the certification of "non-antibiotic", the following matters are notified:




































































